Keeping your data in different baskets? Salesforce over here, MySQL over there, cloud apps scattered like confetti. As a means of protection, it sounds durable. However, today you can centralize and still be safe.
Database integration takes those fragmented chunks floating around, organizes them into something coherent, and delivers a single reliable source, while your team actually gets to go home at reasonable hours.
In this article, we’ll cover:
- What database integration looks like without overcomplicated terms and descriptions.
- Why does it prevent mental breakdowns and financial bleeding?
- Database integration use cases – a vivid illustration of what you can get.
- How to find methods, software, and practices that work for your situation instead of some consultant’s wishlist.
After reading this, you’ll grasp how to reshape your fragmented data into something organized and actionable. So, let’s start!
Table of Contents
- What is Database Integration? (and What It’s Not)
- Why Database Integration is a Business-Critical Strategy
- Common Database Integration Approaches: Choosing Your Path
- Navigating the Challenges of Database Integration
- Database Integration in Action: Real-World Use Cases
- The Modern Database Integration Toolkit
- Best Practices for a Successful Database Integration Project
- The Future of Database Integration: What’s Next?
- Conclusion
What is Database Integration? (and What It’s Not)
Database integration is the process of combining and synchronizing data from various sources into a unified view, ensuring consistency and accessibility across systems, such as databases, cloud platforms, and IoT devices.
What Database Integration Is Not:
- It is not data integration, but its specialized subset, focused on syncing and unifying databases.
- It is not simply copying data or isolated data transfers without coordination and transformation.
- It differs from application integration, which is more concerned with integrating business processes and logic than with unifying data.
- Initiatives for data quality and appropriate data governance must be included in addition to integration.
Database integration is the process of linking multiple, frequently disparate databases to harmonize data; it is not restricted to any one system or format.
Key Concepts
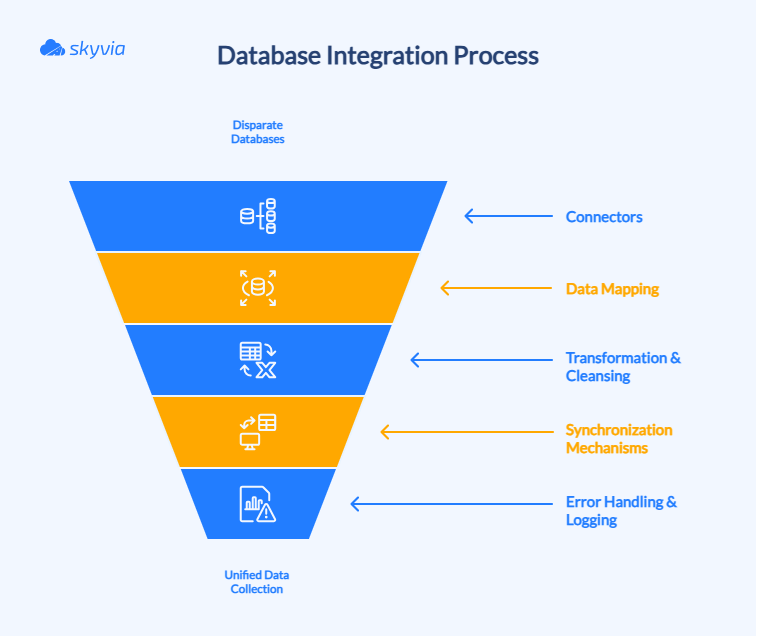
- Connectors: The bridge between databases that don’t naturally speak the same language (relational, non-relational). They’re grabbing information from one side and making sure it lands safely on the other.
- Data mapping: Matching up different database structures so they know how to translate each other’s information. Like making sure “phone number” in one system connects to “contact number” in another.
- Transformation & cleansing: Getting your data ready for the real world. Converting formats, smoothing out the garbage, eliminating doubles, making everything consistent so it actually works as one dataset.
- Database synchronization mechanisms: How you decide to shuffle data around. Maybe you’re doing big batch moves overnight, maybe constant small updates, maybe everything happens instantly. Depends on what you need.
- Error handling and logging: What saves you when things break. It watches everything, shouts when there’s a problem, and documents what happened so you’re not guessing when you need to fix something.
Why Database Integration is a Business-Critical Strategy
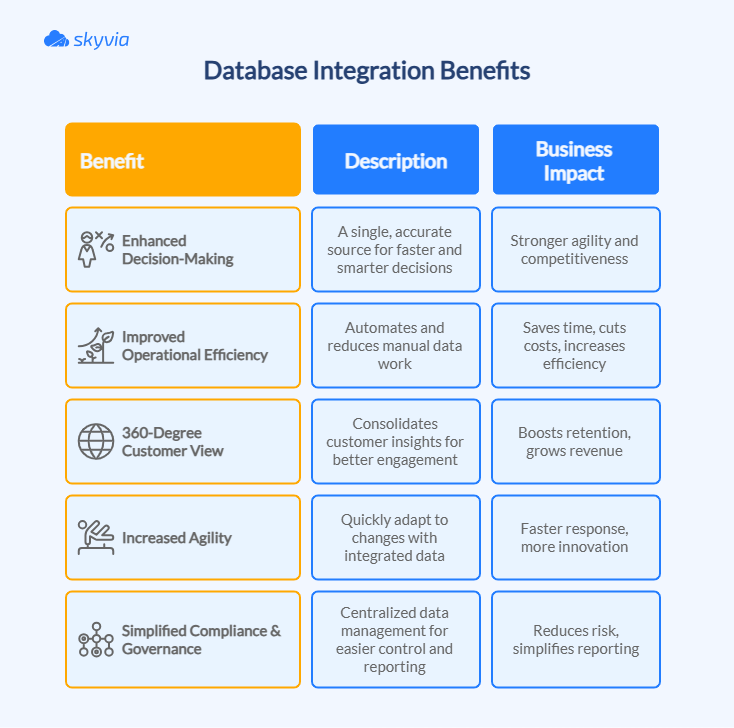
Without integration, managing data across disparate platforms requires you to switch between tabs frequently. Database integration brings everything together, allowing your company to move forward and stop circling around. This is what occurs:
Enhanced decision-making
Scattered data makes choosing your next move about as fun as doing taxes. Pull it all together and boom! You’ve got the real story, hot off the press.
A single source of truth, a centralized repository of reliable data that all teams across an organization, no matter how large, can access, use, and, above all, trust, is the final boss of database integration. Your team quits playing guessing games and starts reading the tea leaves correctly, catching wind of changes before everyone else notices.
Improved operational efficiency
Moving data by hand between systems is about as thrilling as watching grass grow. Integration kicks things into gear automatically, getting your platforms to exchange information without manual intervention, plus it boots out all the do-it-twice waste.
Your people escape the busy work prison and get their hands dirty with what fires them up, solving puzzles that matter and cooking up schemes that turn heads.
A 360-degree customer view
Industry doing somersaults? Cool new platforms winking at you? Integrated information means your business has yoga-level flexibility.
Welcoming new tools to the party, turning up the heat on operations, or riding whatever roller coaster the market builds. It’s all easier than ever when your data doesn’t have an identity crisis.
Simplified compliance and governance
When your data is operating independently in many systems with no one truly monitoring, regulatory compliance becomes messy. By bringing everything together, integration makes your policy more than simply words on paper.
Without a detective’s badge, you can follow what happened to your data, which makes compliance assessments much easier to handle.
Common Database Integration Approaches: Choosing Your Path
Every business is weird in its own special way. It could be that you want everything on your own hardware, where you can keep tabs on it.
It could be you’re willing to move it all to the cloud and let someone else worry about it. Or you’re splitting the difference, mixing on-site with cloud just to be safe. Whatever your style, at least go in with your eyes open about what it means.
On-Premises, Cloud, and Hybrid Integration
- On-premises database integration
You can plant your database firmly on your own turf. Let’s call it a homebody approach. You decide who gets in, what happens when, and how tight the security screws get turned. Works like a charm when you’re managing with legacy systems that have their own personality or when data wandering off keeps you up at night.
- Cloud database integration
Cloud integration lets you dump all that hardware headache on someone else. AWS, Google Cloud, and Azure are basically your new IT department, dealing with the boring stuff like updates, patches, and making sure nothing catches fire. Your systems grow when you grow, shrink when you need to save cash, and you never have to wonder if your software’s getting crusty.
- Hybrid database integration
Can’t commit to one approach? Hybrid integration allows you to play in both fields. Your super-secret data gets to stay in your own backyard, where you can watch it like a hawk, while the rest gets cloud superpowers when you need to scale up fast. A smart move for companies that want to modernize gradually without going cold turkey on control, or when compliance rules restrict access to some data but not others.
Data Integration Methods
Things are becoming a little more technical now, but don’t worry, we’ll serve manageable chunks.
Let’s start with ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) and ELT (Extract, Load, Transform): same letters, totally different game:
- ETL gets everything cleaned up and looking presentable before it comes near your important stuff.
- ELT just moves everything over first and worries about making it presentable once it’s already settled in.
| Aspect | ETL | ELT |
|---|---|---|
| Process | Transform data before loading | Load data first, only then transform |
| Best for | Legacy systems, strict compliance | Modern cloud warehouses |
| Speed | Slower due to pre-load transformation | Faster thanks to cloud computing |
| Flexibility | Limited by upfront transformations | More flexibility (transform only when needed) |
| Security | Custom masking required | Warehouse native controls |
| Use case | Healthcare, finance, and companies prioritizing working with legacy systems | Cloud analytics, AI/LM, big data |
- Real-time vs. batch integration
Data flows at two different tempos: instant gratification or patient waiting. Real-time integration lives in the moment – stopping bad actors in their tracks and customizing experiences while people are still interacting. Batch processing ambles along on its own timeline, handling tasks such as financial reports and old data dumps where urgency isn’t part of the equation.
- API-based integration
APIs help your systems to stop being antisocial. They set up all the connections and make sure everyone’s speaking the same language.
Cloud services, microservices, old databases, new databases, etc., APIs don’t care what you’re working with; they just make it all work together painlessly.
- Change Data Capture (CDC)
CDC wraps up our list. Instead of hauling your whole database around, it just picks up whatever’s new. It’s pretty logical because it’s like buying only what you’re short of instead of doing a full grocery shopping every time.
Database integration is like putting together a toolkit. You want the right gear for whatever job comes up.
- Maybe you’re sticking with on-premises because you trust yourself more than some faceless cloud company.
- Or you’re betting on the cloud because you want to grow without the growing pains.
- Hybrid works when you can’t pick a side and want to hedge your bets.
- ETL, ELT, real-time, batch – they all have their fans for good reasons.
- APIs and CDC are where the smart money’s going these days since they keep you loose and ready to pivot when your data starts doing unexpected things.
Hit the right combination, and your business can actually thrive in chaos instead of just surviving it.
Navigating the Challenges of Database Integration
Pretty much everyone who’s tried to connect different systems has had that same moment of panic. Good news, though, people figure this out all the time, and the problems that seem impossible right now usually have clear-cut solutions.
Common Hurdles
1. Data quality and consistency
Your data’s a mess when different systems can’t agree on basic things – duplicates everywhere, random gaps, and formats that make no sense together. It doesn’t matter how fancy your charts look if the numbers underneath are garbage. The fix is getting your data act together before things hit your central system. Here’s what works:
- Build validation right into your integration process so junk gets caught early.
- Write down some actual rules about data quality and stick to them across everything.
- Check your data regularly, rather than hoping for the best.
- Force everyone to use the same data formats so that systems stop speaking different languages.
The outcome: Information that holds up under pressure, decisions you won’t regret, and analytics that cut through the noise.
2. Schema and data type incompatibilities
Schema mismatches turn integration into a frustrating game because systems interpret data structures completely differently. Fields don’t align, data types conflict, and everything grinds to a halt. Getting your systems to speak the same dialect is the key. The approach:
- Deploy mapping tools that translate between different database structures to prevent information loss.
- Handle schema evolution with registries that track changes and maintain backward compatibility.
- Build adaptive workflows that can withstand structural updates without collapsing.
The outcome: Data keeps flowing smoothly even as your architecture gets more intricate and your models keep changing.
3. Security and compliance
Privacy regulations have made data integration feel like you’re performing brain surgery while someone’s yelling legal threats in your ear.
You need maximum protection without grinding everything to a halt every time you move data around. What keeps you out of hot water:
- Encrypt everything so that your data appears as random letters to unauthorized eyes.
- Maintain detailed records of what happens to your information so auditors can’t catch you off guard.
- Integrate privacy protection into your workflow architecture, rather than treating it as an optional upgrade.
- Stay vigilant, even a bit paranoid, about security gaps and keep regulatory procedures up to date.
The outcome: Information that’s armored like a tank and compliance audits that don’t make you lose sleep.
4. Performance and latency
Fast data beats slow data every single time, but if your integration setup is crawling along like a wounded turtle, speed becomes a pipe dream. Slowdowns become serious problems fast, particularly when you need to make calls that won’t wait until tomorrow. How to get moving:
- Deploy CDC so you’re only processing actual changes instead of reprocessing everything from scratch like some kind of digital hamster wheel.
- Boost performance by parallelizing work and streamlining your transformation logic until it purrs.
- Scale your infrastructure to match demand peaks without falling over.
- Keep your eyes on performance so bottlenecks get spotted and stomped before they spread.
The outcome: Integration processes that keep pace with business reality instead of holding everyone back.
Database Integration in Action: Real-World Use Cases
Seeing someone else navigate the same integration mess you’re stuck in and come out the other side actually functioning?
That’s when you start believing your situation isn’t hopeless after all. Let’s look at some real examples of people who figured it out.
Use Cases Examples
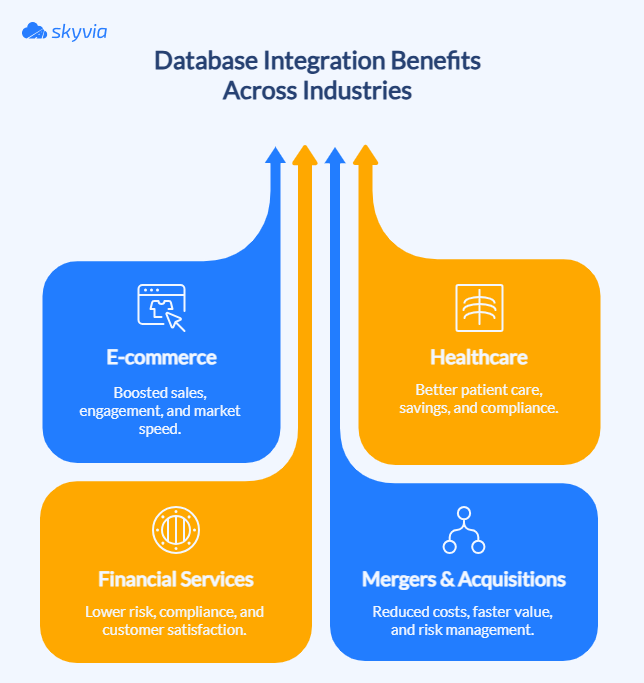
E-commerce
GOintegro, an online business juggling product data in MySQL and client information in Salesforce. Their daily, weekly, and monthly reports were a total pain: every request triggered a chain of manual tasks. On top of that, their internal teams wanted a fuller picture of customer behavior by enriching Salesforce with MySQL data.
Solution: The team used Skyvia to quickly set up automated data flows from MySQL to Google Drive for client reports, and integrated MySQL with Salesforce to enrich client profiles.
Results: Reports now generate automatically, operational costs dropped, errors shrank, and information reaches clients faster. A clear win for automation and efficiency, proving that database integration doesn’t just connect systems, it accelerates business.
Healthcare
Healthcare data comes with more strings attached than a marionette, and AHCA was dealing with a major shift from their old SQL Server setup to Dynamics 365 running in the cloud.
The cloud switch helped them breathe easier about infrastructure, but they weren’t giving up their local SSRS reporting anytime soon, which meant keeping data flowing both ways.
Solution: Skyvia lets AHCA replicate Dynamics 365 data incrementally to SQL Server, supporting ongoing analytics and reporting without forcing a full rebuild of their existing infrastructure. Setting up pipelines was as simple as a few clicks, and connectors covered both current and future integration needs.
Results: AHCA now enjoys automated, up-to-date data replication. Reports refresh reliably, errors shrink, and staff spend less time babysitting ETL jobs. With Skyvia, the transition to the cloud became smooth, practical, and future-ready, a clear win for healthcare analytics.
Financial Services
Billing in financial services can feel like one misstep might make the whole process get messy. The Fortium Partners, a technology leadership services company, needed a way to sync MySQL and QuickBooks Online without building custom scripts for every invoice, something that wouldn’t drain time or budgets.
Solution: Skyvia became the go-to. Using its Data Integration product, Fortium replicated and synced data between QuickBooks Online and MySQL with a straightforward GUI wizard. As a bonus, Skyvia Backup safeguarded sensitive billing data on Microsoft Azure’s secure cloud.
Results: Billing automation became fast, reliable, and worry-free. Timekeeping and invoices now flow seamlessly, errors have dropped, and backups provide peace of mind. Fortium Partners could focus on strategic technology leadership instead of data plumbing.
Mergers & Acquisitions
In M&A projects, creating a single, accurate view of all customer and project data is like assembling a giant puzzle where some pieces keep moving. A4 International, Inc. faced this with a 3D printing client: their engineering projects lived in Streamics on SQL Server, but the Sales team needed real-time visibility in Salesforce CRM.
Their client wanted Salesforce to reflect Streamics data in real time while keeping the legacy system active. Custom REST API coding would have been complex, expensive, and time-consuming, given the volume and number of tables.
Solution: Skyvia offered an elegant, cost-efficient alternative. Using its Salesforce-SQL Server integration, A4 International built a reliable data pipeline that synchronized Streamics data hourly, providing the Sales team with an up-to-date view of engineering and costing workflows without touching the legacy system.
Results: The client achieved a unified customer profile and accurate project visibility across teams. Salesforce became a single source of truth for quotes, orders, and invoicing, while the Streamics system continued running smoothly in parallel. Efficiency, accuracy, and collaboration improved, without the heavy lift of custom coding.
The Modern Database Integration Toolkit
Tool selection success has less to do with fancy features and more to do with finding gear that suits your crew, connects with your current setup, and aligns with your actual processes instead of some idealized workflow chart.
Hit that sweet spot, and your database disorder becomes a coherent system that quits wasting your time and money.
Popular Categories of Tools
| Tool | Key features | Limitations | Pricing/Notes | Typical use case |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Apache Hadoop | Distributed storage (HDFS), batch processing (MapReduce), ecosystem tools (Hive, Pig, Sqoop, Oozie) | Complex setup, infrastructure management, steep learning curve | Free; infrastructure costs apply | Large-scale batch analytics, archival, ETL pipelines |
| Apache Spark | In-memory processing, batch & streaming, MLlib, GraphX, SQL queries | Cluster memory tuning, requires skilled ops | Free; often run on managed platforms (Databricks: $0.20–$0.95/DBU hour) | Real-time analytics, streaming pipelines, ML workloads |
| Skyvia | No-code/low-code, 200+ connectors, real-time sync, ETL/ELT, orchestration | Large-scale volumes may be limited, less developer-centric | Free plan; Basic $79/month, Standard $159/mo, Professional ~$399/mo | SMBs and mixed-skill teams that need easy SaaS and database integration |
| MuleSoft Anypoint Platform | API-led integration, hybrid cloud, prebuilt connectors, governance & monitoring | High licensing & operational cost, steep learning curve | Subscription: Starter, Advanced, Management Solution | Large enterprises with a hybrid cloud or API-first strategy |
| AWS Glue | Serverless ETL, auto-scaling, AWS ecosystem integration, schema discovery | AWS lock-in, less control over infra | Pay-as-you-go (DPUs × runtime) | AWS-native organizations building data lakes and warehouse pipelines |
| Azure Data Factory | Hybrid/on-prem & cloud pipelines, visual authoring, orchestration, SaaS connectors | Pricing complexity, Azure dependency, and learning curve | Based on pipeline runs, DIU-hour, and data flows | Azure-centric enterprises needing hybrid orchestration |
| SSIS | Visual ETL designer, scheduling, error handling, SQL Server integration | SQL Server license required, Microsoft-centric, steep learning curve | Included with SQL Server licenses; Azure IR ~$0.84/hour | Enterprises with Microsoft stacks needing on-prem ETL |
| Pentaho PDI | Batch & real-time integration, visual drag-and-drop, extensible connectors | Limited real-time compared to newer tools, setup effort for enterprise | Free OSS; deployment costs vary | Teams wanting scalable open-source ETL with GUI |
| Apache NiFi | Real-time data flow automation, visual design, and fault-tolerant | Operational complexity for distributed deployment | Free; infrastructure costs apply | Real-time ingestion, streaming pipelines in distributed environments |
Open-source tools
Open-source options give you the freedom to build integration pipelines that match your exact vision, but they come with a “some assembly required” warning label.
You get unlimited customization power, but every bit of installation, maintenance, and optimization becomes your team’s problem to solve.
Apache Hadoop
The granddad who still gets things done in big data land. It knows how to spread storage and number-crunching across bunches of everyday computers. HDFS holds onto your stuff, YARN bosses around your computing power, and MapReduce plows through those monster batch jobs.
It rolls with a whole posse – Hive translates database talk, Pig scripts like a champ, HBase wrestles with NoSQL chaos, Sqoop plays data delivery service, and Oozie keeps workflows marching information.
- Best for: Massive info dumps that don’t wiggle around much, old data storage, building processing chains, and batch analytics that take their sweet time.
- Pros: Battle-tested over the years, grows big without complaining, and has corporate America wrapped around its finger.
- Limitations: Kiss goodbye to simple setup and maintenance.
- Pricing: No direct software licensing. However, you are still paying for the underlying infrastructure.
Apache Spark
It saw what Hadoop was doing and supercharged the whole thing by keeping data in memory. It does batch work, streaming, interactive SQL through Spark SQL, machine learning via MLlib, and graph analytics with GraphX.
- Best for: Real-time analytics, streaming data highways, ML playgrounds, and interactive data spelunking.
- Pros: Speed demon, bends over backwards for different use cases, connects with any data source, and juggles batch and streaming.
- Limitations: Memory optimization will drive you up the wall, and keeping clusters happy takes some serious know-how.
- Pricing: While Spark itself is free, businesses usually run it on managed platforms like Databricks that charge for compute (DBUs), deployment approach, and feature packages. Budget $0.20 to $0.95 per DBU hour (serverless runs higher).
Cloud-Based Integration Platforms (iPaaS)
Cloud iPaaS platforms are basically the smooth operators of the database world. They take care of all the complicated parts so you don’t have to.
They turbocharge your integration work and help you build bridges between all your scattered data, whether it’s living in the cloud or camping out on servers you can actually touch.
Businesses that go this route typically watch their costs drop, see their data get its act together, and can roll with the punches when new integration challenges come knocking without having to micromanage every little detail.
Skyvia

Born and raised in the cloud, this no-code platform focuses on getting you connected fast without the technical gymnastics. With 200+ plug-ins ready to go, it shuffles data around, copies databases, spots changes as they happen, and keeps your workflows humming along.
Real-time syncing means your data never gets old, and those drag-and-drop flow builders make scheduling feel like arranging puzzle pieces.
- Best for: SMBs craving quick cloud integration across their SaaS ecosystem and database collection without the technical circus.
- Pros: Painless to pick up, connects to the whole universe, data never gets stale, and combines integration and orchestration through Data Control and Data Flow.
- Limitations: Enormous data volumes might feel boxed in.
- Pricing: Skyvia offers a Free option for light use (10K records per month, daily scheduling), with paid tiers at Basic ($79), Standard ($159), and Professional (~$399) monthly. Enterprise pricing is available upon request.
MuleSoft Anypoint Platform
The enterprise-grade powerhouse that lives and breathes APIs, designed to play matchmaker between your cloud services and those old-school on-site systems.
It’s got everything crammed into one platform: API management central, security command center, design playground, and analytics brain. Those out-of-the-box connectors and governance features help you rope in even the most scattered enterprise zoo.
- Best for: Heavyweight companies with hybrid cloud mazes or API-first religions.
- Pros: Grows bigger without complaining, security is tighter than a pickle jar, templates to get you rolling, and oversight that doesn’t sleep.
- Limitations: Get ready for some serious coin and a learning curve steeper than Mount Everest, plus setup complexity that’ll have you questioning your career choices.
- Pricing: MuleSoft Anypoint Platform doesn’t publicly list precise numbers. The only thing we need for sure is that there are three subscription options – Integrations Starter, Advanced, and Management Solution.
AWS Glue
Amazon’s serverless data prep service that handles ETL jobs without you having to think about servers or scaling. It automatically adjusts to work with S3 storage, Redshift analytics, RDS databases, and pretty much everything else in AWS’s toolbox.
The smart cookie even figures out your data structure and writes the transformation code for you. Since you only pay when it’s actually working, your costs stay as flexible as a yoga instructor.
- Best for: Organizations that live in AWS land and are building data lakes or stuffing warehouses with fresh data.
- Pros: No infrastructure headaches, self-adjusting performance, clicks perfectly with AWS services, and ETL automation that just works.
- Limitations: AWS becomes your only option, you can’t mess with the engine much, and mastering the AWS ecosystem takes some serious study time.
- Pricing: You pay for Data Processing Units for your ETLs and interactive developer work. Cost comes down to DPUs multiplied by runtime, billed per second with a 1-minute minimum. Your execution class choice (standard or budget-friendly flexible) changes what you pay per hour.
Azure Data Factory
Microsoft’s cloud-scale integration tool that choreographs data movement between cloud services and reliable old servers sitting in your office.
The visual workflow builder and monitoring cockpit keep things accessible for regular humans, while still packing enterprise-grade firepower. It doesn’t discriminate against other cloud platforms either.
- Best for: Organizations living the Azure life who need pipelines spanning cloud and physical hardware, or want low-code analytics orchestration.
- Pros: Melts right into Azure seamlessly, tons of ready-made connections, works across different clouds, and those visual tools actually make sense.
- Limitations: Pricing and pipeline management can get complex, dependent on Azure for best performance, and there is a learning curve for advanced workflows.
- Pricing: Azure Data Factory charges you based on what you actually do: pipeline runs (per 1,000), data shuffling (per DIU-hour), data flow crunching (per vCore-hour), and checking logs (per 50,000 records). Throw SSIS into the mix, and you’re paying for virtual cores and runtime, though Azure Hybrid Benefit can soften the blow.
Self-Hosted Solutions
Self-hosted solutions for database integration offer organizations greater control, customization, and compliance adherence.
SQL Server Integration Services (SSIS)
Microsoft’s ETL flagship for companies that keep their data close to home on SQL Server boxes. It comes packed with drag-and-drop designers, scheduling magic, and bulletproof error catching for when workflows get messy.
- Best for: Enterprise giants running Microsoft, everything that needs ETL that can bench-press massive workloads.
- Pros: Speaks SQL Server’s language fluently, reputation solid as a rock from decades of use, and community backup that never sleeps.
- Limitations: SQL Server licensing costs add up fast, gets cranky outside Microsoft’s playground, and learning the pro moves requires serious dedication.
- Pricing: You’ll find SSIS included with SQL Server Standard or Enterprise licenses, both of which cost money upfront. For Azure deployments, the Integration Runtime charges roughly $0.84 per hour, but that price drops if you tap into Azure Hybrid Benefit.
Pentaho Data Integration (PDI)

The open-source ETL toolkit gives you the best of both worlds – batch jobs and live data streams – all through a point-and-click interface that won’t make you want to scream. It’s got the backbone to handle massive datasets and cloud hookups without breaking into a cold sweat.
- Best for: Development teams who want powerful ETL tools without the price tag, plus the freedom to set up shop however they please.
- Pros: Visual builder that actually makes sense, big data muscles and cloud connectivity, and you can soup it up when vanilla features won’t cut it.
- Limitations: Real-time processing feels a bit dated next to the shiny new competition, and getting enterprise pipelines battle-ready means some serious construction time.
- Pricing: The tool itself won’t cost you a penny, but as with any open-source solution, cost hides in the method of deployment and provider (e.g., AWS, Elestio, etc.).
Apache NiFi
A real-time, open-source visual platform for automating and monitoring data flows. It catches streaming data on the fly, shapes it up however you need, and routes it through your network of scattered systems like a pro.
- Best for: Development teams that need bulletproof real-time pipelines that don’t fall over when spread across multiple systems.
- Pros: Grows with you and can resolve complex routing riddles and data transformations.
- Limitations: Running Apache NiFi across distributed environments can turn into a full-time job, and you’ll need a team that knows its way around.
- Pricing: The tool itself is free, but you will incur costs for the deployment and infrastructure.
Best Practices for a Successful Database Integration Project
Ever felt that database integration is more like pushing a boulder uphill, and you have no idea which data gods punished you so hard?
There may be a lot of different reasons why you are suffering so much, and sometimes even sets of reasons combined to drive you crazy (spoiler: it only seems so, everything can be fixed or prevented). Before you rush into action, you need to understand what connects to what and why.
1. Start with a clear strategy
Don’t even think about mapping fields yet. Seriously, stop. What does winning look like for this project? You need to nail that down, whether it’s speeding up analytics, pulling together a complete picture of your customers, or getting instant notifications when stuff goes down. Once you know where you’re headed, dig into your data sources.
What formats are we dealing with? How big is this thing going to get? Pull your stakeholders into the conversation right away, too. Tech decisions need to match up with what the business actually wants, plus you’ve got compliance boxes to check.
2. Prioritize data governance
Governance may feel mundane in comparison to the integration process. Yet, it’s better to resist the temptation to shelve it for later.
It’s the foundation everything else sits on. So, let’s make sure it is strong and can withstand all the challenges you’re going to put it through later. Start with the basics:
- Ownership structure.
- Access permissions.
- Quality expectations.
Then proceed with building your quality machinery into the system itself:
- Validation that rejects nonsense.
- Deduplication that keeps your database from turning into a hall of mirrors.
- Standardization, so California and CA mean the same thing.
- Keep tabs on data lineage, too, because “where did this come from” is a question you’ll get asked constantly.
- Regulations aren’t background noise either. GDPR, HIPAA, whatever’s relevant, shape how you build things, not just how you document them afterward.
All of these are bricks of your database integration process.
3. Thoroughly test and validate
Turn testing into something you do automatically, not a special occasion. Start checking things immediately and keep at it forever. Test components in isolation before anything else. Every connector gets its own trial run, each mapping gets scrutinized alone, and transformations get tested individually. Does this piece function? Perfect, keep moving.
Then connect all the dots and run everything together, because that’s when you discover which bright ideas were actually terrible. Automation takes care of the tedious, recurring checks. Manual testing catches the bizarre edge cases that slip through scripts. And have your rollback strategy figured out before you need it.
4. Monitor and maintain
No matter how bad everyone dealing with database integration processes would want, “set it and forget it” is not how it works. Although automation can save you time and effort, it’s still a garden that needs care.
- Keep an eye on your pipelines, dashboards, and alarms.
- Monitor throughput and freshness.
- Plan maintenance as your data volume increases.
Additionally, get ready for incidents so you can quickly address problems before they have an impact on operations or reports.
5. Choose the right partner
It’s imperative to choose a vendor who can understand your mess, is familiar with the peculiarities of your sector, and realizes that compliance is a must. Look for solutions that have all the means for adequate training, good support, automation that works, security that passes inspection, and connectors that cover your bases both now and in the future.
The right tool changes everything. Without it, integration becomes this endless slog that eats months of your life. With it? You’ve got a fighting chance at keeping things sane and actually shipping on time.
| Best practice | Key actions | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Clear strategy | Define goals, assess data, set KPIs | Aligned efforts, focused outcomes |
| Data governance | Ownership, policies, quality, compliance | Reliable, high-quality, compliant data |
| Test and validation | Component & end-to-end testing, rollback prep | Smooth rollout, minimized risks |
| Monitor & maintain | Continuous monitoring, logging, and incident planning | Sustained reliability, proactive fixes |
| Right partner | Evaluate experience, support, and compliance | Efficient deployment, reduced headaches |
The Future of Database Integration: What’s Next?
Gazing into database integration’s future feels like attempting to predict a book’s ending after reading page one. What’s rolling down the pipeline isn’t some far-off dream, though; it’s basically knocking on your door already.
More intelligent, speedier, and adaptable methods are flipping the script on how businesses manage information, and keeping up might be the difference between cruising along and getting buried under problems.
AI and Machine Learning
AI already identifies problems that humans usually tend to overlook (everyone braces themselves at this point), suggests solutions, and anticipates slowdowns before they occur. While your queries are executing, machine learning optimizes them, automatically reshapes schemas, identifies questionable patterns, and suggests more effective ways to process data.
All things considered, integration procedures are becoming more self-sufficient, which significantly lessens the requirement for manual monitoring while preserving accurate, fast, and reliable data.
Data Fabric and Data Mesh
The data architecture we’re used to today will change. Maybe something will disappear altogether. So far, we can see that two already powerful concepts gain even more relevance: data fabric and data mesh. While the first one offers a centralized, unified view of all sources, the second gives individual business units the ability to own their data, promoting self-service and agility.
Some businesses went even further to get the best of both worlds. They combine the two strategies to get what some refer to as “Data Fabresh,” a hybrid that combines decentralized freedom with central power.
The rise of real-time data
It’s not that people aren’t ready to wait for answers; it’s that they can’t afford that anymore. And why would they if there is streaming infrastructure, event-based systems, and CDC? Fresh information is a table-stakes requirement for staying relevant these days.
Prioritize dashboards that show what’s happening right this second, fraud prevention that goes off when trouble starts brewing, and customization that adapts in real-time.
Conclusion
What database integration does is take your messy, disconnected information and transform it into a clean flow your team can trust and use. Decision-making gets sharper, tedious tasks run themselves, and those meaningless numbers become clear actions you can take.
Connect your data sources, keep them in sync, make them harmonize, and suddenly you’re not just more efficient. You’ve got a live view of how your business is actually running right this second. The whole point is getting your data to work for you instead of against you – solid, available, ready whenever you need answers.
Wonder if this has to be complicated? It doesn’t. Skyvia’s cloud-based platform skips the coding entirely, letting you wire up and orchestrate databases without fighting with infrastructure headaches.
F.A.Q for Data Orchestration
What is a data orchestration framework?
It is a structured system composed of tools, components, and processes designed to automate, manage, and monitor the flow of data across diverse sources, transformations, and destinations within an organization.
How do you implement data orchestration?
Set outcomes/SLAs, inventory sources/targets, pick a tool, design DAGs, add tests, data contracts, and policies, set triggers/schedules, wire logs/alerts, pilot & backfill, finally iterate, document, and scale.
What is the difference between data orchestration and data automation?
Automation runs a task (e.g., an ETL job). Orchestration coordinates many automated tasks end-to-end.