If your company’s data is still piling up like a mountain of paperwork on the desk, and there’s more and more coming in every day, but most of it’s never even touched, the data automation story is for you.
Just imagine a kitchen where everything’s prepped and cooked automatically, the dishes come out perfect, and you barely have to lift a finger.
Data automation is like that. It’s about:
- Freeing up time.
- Cutting out the mistakes.
- Turning all that raw data into something you can actually use, right when you need it.
In this guide, we’ll walk through:
- The core ideas behind data automation.
- How can it help streamline processes?
- Practical ways to start using it to transform the workflows.
From automating simple tasks to creating more complex, integrated systems, we’ve got you covered.
Ready to start turning all that data into something useful? Let’s dig in.
Table of Contents
What is Data Automation?
This term means using technology to handle data-related tasks without human intervention. It handles tasks like:
- Data collection.
- Transformation.
- Analysis.
This approach allows the info to flow from one place to another seamlessly without anyone working manually.
The Role of ETL
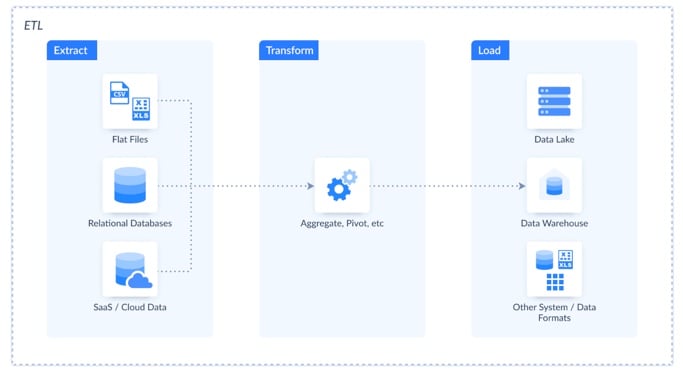
One of the best-known examples of data automation is ETL (Extract, Transform, Load). It’s like a well-oiled conveyor belt in a factory, where raw materials (data) are extracted, transformed into the right form, and then loaded into a warehouse or system ready for analysis.
ETL automates the movement of data between systems, ensuring it’s where it needs to be and in the right format.
Data Automation vs. Data Orchestration
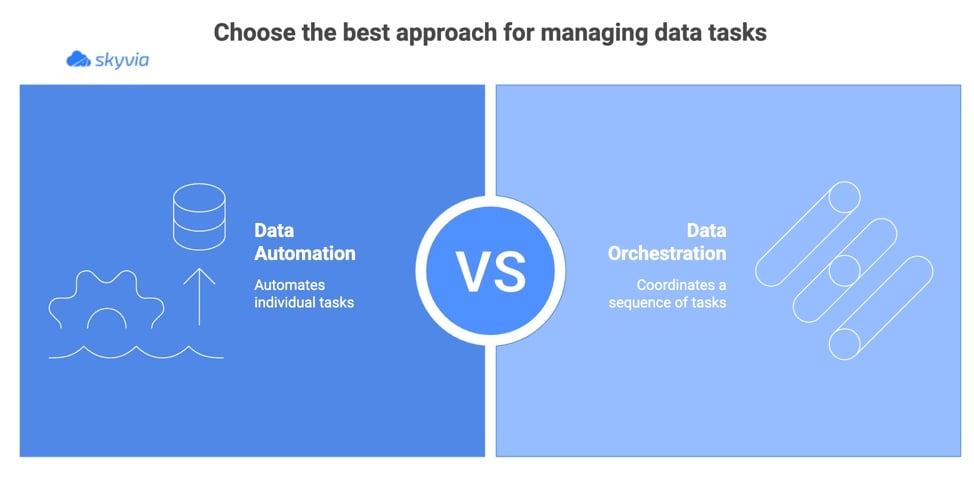
While data automation focuses on automating individual tasks, data orchestration is about coordinating a sequence of them.
Imagine you’re running a kitchen: automation is like the oven cooking the chicken automatically, while orchestration is the entire cooking process, getting the chicken, the potatoes, the veggies, and everything else in sync, making sure each part of the meal is done at the right time.
Why is Data Automation Crucial for Modern Businesses?
Increased Efficiency and Productivity
Most teams drown in repetitive tasks. Copying data, fixing imports, reconciling reports. Automation steps in here, quietly handling the routine so people can get back to higher-value work. The shift is simple but powerful:
- Less time wasted.
- More energy on what actually grows the business.
Improved Data Quality and Accuracy
Automating data processes means removing the risk of human errors. This approach leads to cleaner, more reliable data. The fewer mistakes you have in the pipeline, the more trustworthy the insights become, giving a solid foundation for decision-making.
Faster Decision-Making
In business, speed often wins. Automation ensures data is available in near real time, so leadership can act quickly and with confidence.
When the information pipeline is seamless, decision-making stops being reactive and starts being proactive.
Enhanced Scalability
Manual processes might work when data volumes are small, but they don’t stretch. Automation scales naturally.
Whether you’re doubling customer records or tripling transaction data, the systems keep pace without demanding more headcount or late nights from your team.
Cost Savings
Errors cost money, and so does rework. By cutting out both, automation pays for itself. It also frees up budget and people for the initiatives that matter, innovation, growth, and customer experience, rather than patching up data mishaps.
Empowering AI and Machine Learning
Clean, well-organized data is the backbone of effective AI and machine learning models.
Automated pipelines ensure the data is high quality and ready for analysis, helping AI systems learn faster, perform better, and deliver real value to your business.
How Does Data Automation Work? The Core Components
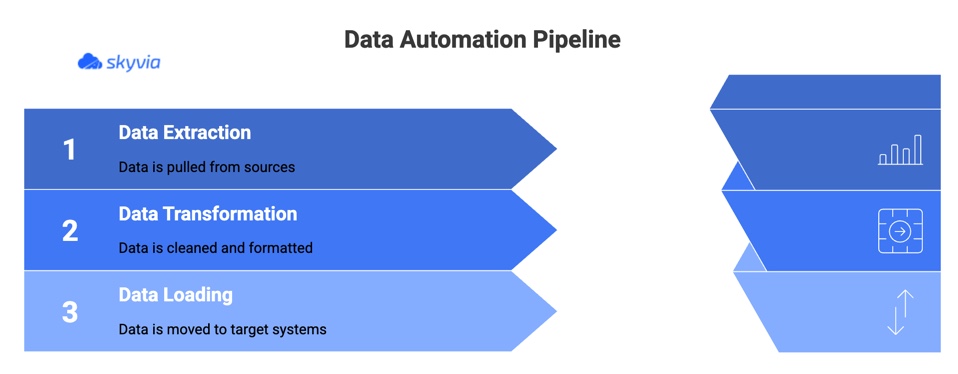
At its core, data automation runs on a simple idea: build a pipeline that moves information from point A to point B without constant human involvement. Each stage of that pipeline (extracting, transforming, and loading) can be automated to keep data flowing smoothly and reliably. Let’s break it down.
The Data Pipeline
The pipeline is like the plumbing for the information. It connects all the sources where data lives, processes it into the right format, and delivers it to the systems where it’s needed.
Automation keeps this pipeline running consistently, without someone having to open the valve every time.
Data Extraction
This is where data gets pulled in from different places. APIs, databases, SaaS apps, or cloud storage. Instead of manually exporting and importing files, automated extraction tools connect directly to those sources and fetch the data on a schedule or in real time.
Data Transformation
Raw data is like the ingredients that need to be prepared before hit them to the kitchen.
Automation handles the heavy lifting here by cleaning up duplicates, validating formats, and reshaping the info into something that analytics tools and warehouses can actually use.
Data Loading
Once the data is ready, automation takes care of moving it into the target system (a data warehouse, data lake, or even a business app).
This step ensures the right people always have the latest information at their fingertips, without waiting for manual uploads.
Automation in Action (Triggers)
Automation doesn’t just run in the background. It responds to how your business works.
- Scheduled Automation. Think nightly reports or end-of-month summaries. Set it once, and it runs like clockwork.
- Trigger-Based Automation. Workflows that kick off when something specific happens, like a new customer record being created or a file showing up in cloud storage.
- Real-Time Streaming. Data flows continuously as it’s generated, ideal for use cases where timing is everything (fraud detection, live dashboards, IoT monitoring).
Real-World Examples and Use Cases of Data Automation
Think of this as showing the “magic in motion,” where automation isn’t theory but working hard behind the scenes to solve real business problems.
Below are some scenarios you’ve probably seen (or will see) in practice and how automation handles the grunt work.
Oleksandr Khirnyi, Chief Product Officer at Skyvia said: “The launch of the Automation product represents a significant advancement in our mission to optimize data-related processes and help businesses achieve greater results with minimal effort. With a user-friendly visual designer, intuitive logic creation, and automatic error detection, we empower organizations to automate complex operations while reducing manual involvement.”
Marketing Automation
One of the friendliest use cases: trigger personalized emails or campaigns based on what customers do.
If someone abandons a cart, automation can fire off a gentle reminder email. Or when a user reaches a usage milestone, a “Congrats + upsell” message can be triggered automatically. No manual list exports or guesswork required.
Example: integrating Mailchimp with your data warehouse allows triggered email campaigns to respond instantly to customer behavior.
Financial Reporting
Instead of pulling together spreadsheets, balancing ledgers, and reformatting charts manually, automation can generate and distribute reports (income statements, cash flow, and balance sheets) on a schedule. This gives finance teams time back to analyze trends rather than wrangle data.
Example: Cirrus Insight automated the integration between Salesforce and QuickBooks. By connecting the two systems, their finance team no longer had to manage duplicate entries or manual exports, and reporting became faster and more accurate.
Fraud Detection
Here, you need speed and vigilance. Automation continuously monitors transactions, flags anything that looks suspicious, and raises alerts in real time. No waiting for someone to run scripts overnight.
Sales Operations
Dirty CRM data destroys efficiency. Automation can continuously dedupe, validate, and sync records so your sales team always sees accurate, up-to-date customer info. That means fewer surprises in pipeline reviews and cleaner handoffs between reps.
Supply Chain Management
In inventory-heavy setups, automation tracks stock levels, reorders when thresholds are hit, and routes new orders to suppliers. That “out of stock” panic moment? Much less frequent when your system is already watching the shelves.
Example: Redmond Inc. has automated their inventory management by syncing Shopify data with internal systems, ensuring real-time updates and efficient order processing.
Healthcare
Healthcare workflows are complex and data-sensitive. Automation helps manage patient records, sync data across systems (EHR, billing, lab systems), and feed analytics for better decision-making.
Example: A clinical-trial service provider automated integration of backend systems, CRM, ad platforms, and Excel files, freeing up teams from manual Excel juggling.
Top Data Automation Tools and Technologies
So, now you know that automation is worth it. But the big question becomes: what tools are out there to actually make it happen?
The landscape is wide (from no-code apps anyone can use to heavyweight cloud services built for data engineers). Let’s walk through the main categories and what they bring to the table.
No-Code/Low-Code Platforms
This is usually where people start dipping their toes into automation. Tools like Zapier easy connect apps for quick wins.
Send a Slack ping when a new lead comes in, copy attachments into Google Drive, that sort of thing. But when the needs get more data-heavy, something like Skyvia comes into play.
The platform sits in that sweet spot between simplicity and power: it lets non-technical users build workflows that move and transform data across 200+ CRMs, databases, cloud apps, and warehouses without writing code.
The drag-and-drop style keeps it approachable, but under the hood, it handles complex integrations and scheduling just as well as more technical platforms.
The key point? No-code doesn’t have to mean “toy solution.” With the right tool, you can solve serious data problems without needing a team of engineers.
ETL/ELT Tools
When the job gets too big for simple workflows, you move into the ETL/ELT world. Tools like Fivetran, Talend, or Stitch are built for serious data integration:
- Pulling information from dozens (sometimes hundreds) of sources.
- Transforming it into a consistent format.
- Loading it into a warehouse.
They’re designed to handle scale, with connectors for everything from SaaS apps to legacy databases.
The trade-off? They usually require more setup and budget, but they pay off when your business lives and dies by analytics.
Cloud-Based Solutions
When talking about the big clouds (AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud), their data automation services, like AWS Glue, Azure Data Factory, or Google Dataflow, are incredibly powerful and can crunch massive workloads, but they’re not exactly plug-and-play. You’ll likely need engineers to configure them, write code for custom logic, and keep everything running.
Note: If you already run most of the stack in one of these clouds, though, using their automation tools can make a lot of sense.
Open-Source Options
For the DIY crowd, there’s a whole world of open-source frameworks like Apache Airflow or Luigi. These give you maximum flexibility to design and schedule workflows exactly the way you want.
They’re hugely popular with data engineering teams. These solutions integrate well with custom scripts and pipelines.
The catch: you’re on the hook for maintenance, monitoring, and scaling. So they’re great if you’ve got the technical muscle, but overkill for those who just want to automate a few reporting tasks.
Key Features to Look For
No matter which category of tool you choose, a few core qualities make the difference between something that looks good on paper and something your team will actually thrive with.
Scalability
Your data volume today is almost guaranteed to grow tomorrow. A tool that feels fine for a few thousand records might buckle under millions.
Look for platforms that scale gracefully, not just in terms of storage, but also in performance, speed, and pricing model.
Ease of Use
It doesn’t matter how powerful the tool is if no one wants to use it. A clean interface, an intuitive workflow builder, and helpful documentation go a long way.
Ideally, both technical and non-technical users should be able to get value from it without endless training sessions.
Security and Compliance
Data is often the most sensitive asset. The right tool should support encryption, role-based access, audit trails, and compliance with frameworks like GDPR or HIPAA if that’s relevant to your industry.
Integration Capabilities
This one is non-negotiable: the tool should play nicely with the apps and systems you already rely on. Whether it’s your CRM, ERP, marketing platforms, or a data warehouse, seamless connectors make automation possible without endless custom coding. Bonus points if the tool has an open API, so you’re not stuck when your tech stack changes.
Flexibility and Customization
Not every process fits into a prebuilt template. The best tools let you add custom logic, transformations, or conditional workflows so automation bends to your business rules, not the other way around.
Monitoring and Reliability
You don’t want to find out a pipeline broke only when someone spots missing data in a report. Look for dashboards, alerts, and logging features that keep you in the loop. Reliable automation is invisible. It just runs until you need to know otherwise.
Quick Checklist Before You Choose
Ask yourself (and the vendor) these five questions:
- Will this tool still serve us when our data volume doubles (or triples)?
- Can my non-technical teammates pick it up without weeks of training?
- Does it meet the security and compliance standards we can’t compromise on?
- Does it integrate cleanly with the systems we rely on most?
- How will I know if something breaks, and how quickly can I fix it?
If a tool clears all five, it’s a solid candidate. If it stumbles on more than one, chances are you’ll feel the pain down the road.
How to Develop a Data Automation Strategy
Here, let’s get back to our “kitchen” scenario. Building a data automation strategy is a bit like renovating a place where you cook every day. Don’t rip everything out at once. Start by fixing what slows you down most.
It’s about picking the right spots, laying a solid foundation, and then expanding piece by piece. Think of it as creating a roadmap where small wins add up to long-term efficiency.
Identify and Prioritize
First, figure out where your team spends the most time on repetitive or error-prone tasks. Maybe it’s reconciling spreadsheets, maybe it’s exporting reports every week.
These are your “low-hanging fruit” (the places where automation can deliver the biggest return quickly).
Define Clear Objectives
Automation for automation’s sake doesn’t help anyone. Be specific: do you want to cut processing time in half, reduce manual errors by 80%, or improve reporting speed? Clear goals make it easier to measure success and get buy-in from stakeholders.
Choose the Right Tools
There’s no one-size-fits-all answer here. The right choice depends on:
- The team’s technical skills.
- Budget.
- The systems you already use.
A no-code tool might work great for operations, while a cloud-native platform could be better for large-scale data engineering. Match the tool to the job, not the other way around.
Start Small and Scale
Don’t try to automate everything on day one.
- Pick one pilot project.
- Get it running smoothly.
- Use that success story to build momentum.
Once people see the value, it’s much easier to expand into other areas without resistance.
Monitor and Optimize
Automation isn’t “set it and forget it.” Keep an eye on performance, add monitoring or alerts, and adjust as workflows evolve.
Businesses change, and so does data. The best strategies treat optimization as an ongoing process, not a one-time project.
The Future of Data Automation: Trends to Watch
If we get back to our “kitchen,” the future is closer to running a restaurant where much of the service works itself.
Orders get routed automatically, dishes are prepared in sync, and the system adjusts when there’s a sudden rush.
Instead of manually coordinating every step, you set the menu and standards, and intelligent systems handle the execution.
AI and Machine Learning
AI, as the head chef, notices when ingredients are off, when a dish doesn’t look right, or when demand is about to spike.
In data terms, that’s anomaly detection, predictive analytics, and smarter automation that prevent problems before they hit the table.
Agentic AI
This is like having managers on the floor who don’t need you to tell them every move. They see that a big group just walked in, reassign staff, and make sure orders flow without bottlenecks.
In data pipelines, agentic AI can reroute jobs, optimize resources, and manage workflows dynamically (without waiting for human approval).
Declarative vs. Imperative Approaches
In the past, you had to spell out every kitchen step: chop onions, sauté, plate, serve. Now you can declare, “I want a medium-rare steak with sides,” and let the system figure out the steps.
In data automation, this means you describe the outcome, and the platform handles the execution.
Data Mesh and Data Fabric
Picture a restaurant group with multiple kitchens sharing resources. A data mesh is like giving each kitchen control over its own menu while still aligning on quality standards.
A data fabric is more like a central supply chain that ensures all kitchens get fresh ingredients on time. Either way, automation keeps everything flowing smoothly across the whole operation.
Conclusion
Of course, data automation saves users time. But, firstly, it’s about building a foundation where efficiency, accuracy, scalability, and smarter decision-making come naturally.
From cleaner data to faster reporting and fewer errors, the benefits add up quickly, freeing teams to focus on strategy instead of busywork.
It’s no longer a “nice to have” add-on. Businesses that embrace automation now set themselves up to compete in an environment where speed and precision make all the difference.
The next steps are simple:
- Start small.
- Prove the value.
- Expand from there.
Pick one process that’s eating up time, automate it, and watch the impact ripple through the team.
And, sure, start the data automation journey with the correct solution.
F.A.Q. for Data Automation
What is a simple example of data automation?
Automatically sync customer data from a CRM to a marketing tool, ensuring teams always work with up-to-date information without manual exports or uploads.
Is data automation the same as ETL?
Not exactly. ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) is a type of data automation that focuses on data integration. Data automation encompasses a broader range of functions, including reporting, workflows, monitoring, and more.
What are the key benefits of automating data processes?
Automation saves time, reduces errors, improves data quality, scales with growing needs, provides real-time insights, and enables teams to focus on higher-value work.
How can my business start with data automation?
Begin by identifying repetitive, error-prone data tasks. Set clear goals, choose tools that fit your needs, and start small with a pilot project before scaling.