Summary
- ER/Studio – enterprise-grade modeler with strong collaboration, governance, and full conceptual-to-physical support.
- erwin Data Modeler – detailed enterprise modeling with automated DDL and deep governance/metadata integration.
- SAP PowerDesigner – multi-domain modeling across data, process, and apps with rich collaboration and metadata.
- DbSchema – easy, cross-platform designer with multi-DB support, schema sync, and documentation tools.
- Lucidchart – cloud diagramming with real-time collaboration, ERDs, and broad workflow visualization.
When information exists in silos across dozens of tables with relationships more tangled than a Christmas light string, it’s not because of bad luck or market forces going rogue; it’s a need for data modeling tools.
They are the architects’ drafting software for the digital world, letting you map out exactly how your customer data connects to orders, how inventory relates to suppliers, and where every crucial piece of business intelligence fits into the bigger picture.
We’ve rolled up our sleeves and put the top contenders through testing: covering everything from user experience to advanced features, pricing to performance. Let’s find the tool that fits your data specification, budget, and technical requirements, all at once.
Table of contents
- Why Data Modeling Tools are Non-Negotiable for Data Quality
- Key Features to Look for in a Data Modeling Tool
- The Best Data Modeling Tools for 2026: A Detailed Comparison
- At-a-Glance: Feature Comparison Table
- How to Choose the Right Data Modeling Tool for Your Project
- Putting Your Model to Work: Integrating with a Data Platform Like Skyvia
- Conclusion
Why Data Modeling Tools are Non-Negotiable for Data Quality
When data starts running wild, it’s time to set house rules. Modeling tools don’t just nudge, they lay down the law.
Here’s why these tools have become the difference between data that works for you and data that works against you.
The Blueprint for Consistency
Neatness is nice, but the point is protection. Constraints catch mistakes at ingestion, so reports don’t go off the rails. If a duplicate slips by or a link targets a non-existent row, the model’s guardrails block it instantly.
These tools enforce data integrity through:
- Primary keys assign a unique ID to every record to avoid repeats.
- Foreign keys validate that relationships match real rows in the target table.
- Unique constraints enforce uniqueness in specific attributes, such as email addresses, to avoid duplicates.
- Check constraints enforce domain rules (ranges, patterns).
Enhanced Collaboration
Modeling tools bridge the boardroom and the build room. Stakeholders can peek under the hood of their request, while engineers get clear, testable requirements without endless back-and-forth.
Reduced Errors & Faster Development
Remember the days of hand-coding SQL scripts? Data modeling tools have made that nightmare mostly obsolete.
Forward engineering capabilities automatically generate database schemas, stored procedures, and documentation from your models, no more typos in table names or forgotten foreign keys that break everything at the least suitable moment.
This automation isn’t just about speed (though cutting development time in half never hurt anyone). It’s about consistency and reliability.
When the tool generates your scripts, every table follows the same naming conventions, every relationship is defined correctly, and the documentation actually matches what’s in production.
Clear Documentation and Governance
Having a clear map of where every piece of sensitive information lives and how it flows through your systems deserves more acclaim.
It saves companies when auditors pay a visit, it makes onboarding for new team members easier, and, above all, it lets everyone sleep soundly.
Data modeling tools automatically capture metadata, data lineage, and business definitions in one centralized location. What is in it for you? Documentation ceases to be a necessary evil and becomes your data’s autobiography. The prefix “auto” is the best part here.
Key Features to Look for in a Data Modeling Tool
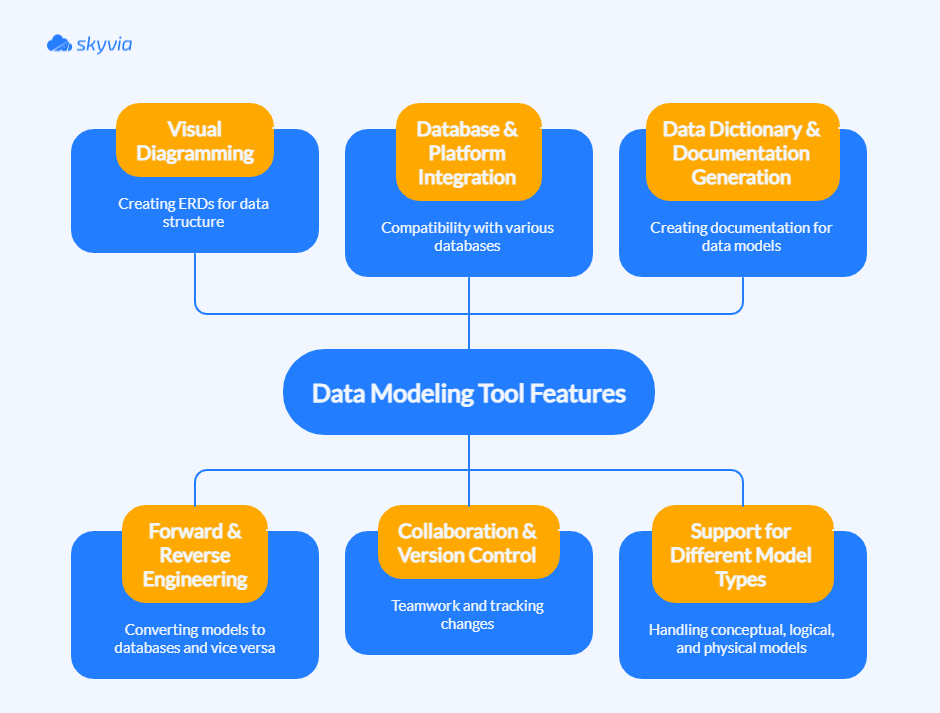
With the why in place, here’s the what. The right tool should make models easy to view, easy to modify, and easy to share across teams and platforms without breaking consistency or governance.
Visual Diagramming (ERDs)
If you want an interface that lets you design and understand schemas at a glance, look for intuitive ERDs (Entity-Relationship Diagrams) with:
- Drag-and-drop editing.
- Clear rendering of entities, attributes, keys, and relationships.
- Support for common notations like Crow’s Foot and Chen.
The best tools layer views so you can toggle between conceptual, logical, and physical diagrams, explore models interactively, and export visuals for stakeholders.
Forward & Reverse Engineering
- Forward engineering turns models into DDL (Data Definition Language) scripts automatically, cutting manual errors and speeding delivery.
- Reverse engineering pulls live schemas back into the model for analysis, documentation, and redesign, which is essential for legacy modernization and impact analysis.
Together, they keep design and implementation in sync through the lifecycle. Version histories attached to these flows help you track changes and roll back safely.
Database & Platform Integration (MySQL, PostgreSQL, etc.)
Multi-DBMS support is a new basic minimum in 2025. It’s best when your tool can connect to MySQL, PostgreSQL, Oracle, SQL Server, and NoSQL where needed, and work with cloud data platforms like Snowflake and Redshift for forward/reverse engineering and metadata sync.
Collaboration & Version Control
Modeling takes a squad. Prioritize:
- Live co-editing with conflict resolution.
- Version history and change tracking.
- Side-by-side model diffs.
- Branching for safe experiments.
Tie in Git (distributed version control system) or a built-in repo to keep models in step with code, cutting rework and smoothing handoffs for architects and DBAs.
Data Dictionary & Documentation Generation
Automated doc generation to HTML, PDF, or a wiki is critical for audits, onboarding, and simple day-to-day governance. An embedded data dictionary should capture:
- Definitions.
- Data types.
- Business rules.
- Provenance for every element.
Rich metadata supports lineage and keeps business and technical teams aligned on meaning and usage, which directly improves data quality.
Support for Different Model Types (Conceptual, Logical, Physical)
Modeling comes in layers:
- Conceptual = the business view, no tech clutter.
- Logical = attributes, types, and relationships, still vendor-neutral.
- Physical = tables, indexes, constraints for a target DBMS.
Pick a tool that supports all three to bridge the requirements to build and sharpen accuracy and communication.
The Best Data Modeling Tools for 2026: A Detailed Comparison
Prepare for a deep dive into the non-uniform waters. We divided all the tools we’re about to dissect into four buckets: enterprise and commercial, for small to medium businesses, free and open-source, and specialized ones, to make this search organized. Let’s go.
Top Enterprise & Commercial Tools
| Aspect | ER/Studio | erwin Data Modeler | SAP PowerDesigner |
|---|---|---|---|
| Best for | Enterprise, cross-platform, metadata | Enterprise governance, data intelligence | Enterprise architecture, multi-domain |
| Key Features | ERDs, forward/reverse engineering | Multi-model support, DDL generation | Business/process modeling, lineage |
| Pros | Powerful reconciliation, metadata | User-friendly, strong reverse engineering | Scalable, governance-rich |
| Cons | Windows only, complex UI | Pricey, some cloud DB limits | Complex, costly, steep curve |
| Pricing (approx.) | $2,687-$3,693/user | Available at a quote | From $30/user/month |
| Learning Curve | Moderate to steep | Moderate | Steep |
ER/Studio
Best for
- Large enterprises that need cross-platform data modeling and collaboration.
- Complex logical and physical data modeling with strong support for metadata management.
- Organizations that require data governance and impact analysis capabilities.
Key Features
- Visual design through ERDs.
- Forward and reverse engineering capabilities for popular DBMS.
- Collaboration with version control and model comparison.
- Metadata and data dictionary management.
- Supports logical, conceptual, and physical models.
- Integration with cloud and on-premises databases.
Pros
- Powerful support for model reconciliation and versioning.
- Strong metadata repository with impact analysis.
- Mature, enterprise-grade toolset widely adopted.
- Good multi-team collaboration support.
Cons/Limitations
- Windows-only desktop application.
- Pricing can be expensive for smaller organizations.
Pricing
- Commercial pricing typically starts around $3,000 – $4,000 per user (perpetual license).
- Subscription options and enterprise licenses are available upon request.
Learning Curve
Pretty high learning curve due to complexity makes ER/Studio best suited for experienced data engineers. Yet, the tool balances this a bit with extensive documentation and an active user community.
erwin Data Modeler
Best for
- Enterprises focused on governance, policy compliance, and rich metadata catalogs.
- Complex logical and physical data models and automated script generation.
- Teams that need integration with data intelligence suites.
Key Features
- Supports conceptual, logical, and physical data modeling.
- Forward and reverse engineering for major databases.
- Automated DDL generation.
- Metadata-driven design with a data dictionary.
- Integration with data governance and business glossary tools.
- Collaboration through web portals (repository required).
Pros
- User-friendly, intuitive interface.
- Strong reverse engineering and model synchronization.
- Robust metadata and data governance integration.
- Highly scalable for large enterprises.
- Active user community and professional support.
Cons/Limitations
- Windows-only option.
- Some users report occasional UI lag and complexity.
- Advanced cloud database support is limited compared to newer tools.
- Limited out-of-the-box multi-language support.
Pricing
- The vendor doesn’t publish its pricing list. You will need to make a request.
Learning Curve
- Moderate learning curve with many features suitable for users from intermediate to expert levels.
- Rich tutorials and training programs are available.
SAP PowerDesigner

Best for
- Large enterprises that need comprehensive enterprise architecture and data modeling, including business process and requirement modeling.
- Multi-domain modeling for business, data, process, and application architecture.
- Integrated modeling and metadata management to support governance.
Key Features
- Supports conceptual, logical, and physical data models with multi-domain architecture modeling.
- Business process modeling and requirements analysis.
- Strong metadata repository and data lineage capabilities.
- Role-based security and enterprise repository.
- Integration with SAP and other enterprise systems.
- Automated code generation supports .NET, VB, JSF, among others.
Pros
- Adaptable deployment choices, such as cloud and on-premises.
- Incredibly scalable for intricate business models.
- Deep connection between the fields of IT architecture and business.
- Impact analysis, traceability, and strong governance.
Cons/Limitations
- Configuring and implementing it can be challenging.
- For SMBs, a higher TCO could be prohibitive.
- When compared to lighter, more recent tools, SAP PowerDesigner’s UI/UX can seem antiquated.
- Windows-only option.
Pricing
- Subscription pricing starts at approximately $30 per user per month for standard plans.
- Enterprise plans and customization can raise costs significantly (up to $50+ per user/month).
- Implementation costs vary widely; SMBs: $5K-$15K; Enterprises: $20K-$50K+.
Learning Curve
- Non-technical users may find the learning curve quite steep.
- Requires training and experienced governance teams for effective use.
Best Tools for Small to Medium Businesses
| Aspect | DbSchema | Lucidchart | Navicat Data Modeler |
|---|---|---|---|
| Best for | Cross-platform, SQL/NoSQL design | Cloud-based diagramming & collaboration | Multi-DBMS, affordable data modeler |
| Key Features | Visual design, schema sync, Git version control | ERDs, templates, real-time collaboration, and AI assist | Multi-notation, forward/reverse engineering, cloud DB support |
| Pros | Easy to use, multi-DB support, offline sync | Easy & intuitive, cloud, sharing | Multi-DBMS, affordable, comprehensive |
| Cons | No cloud DW support, UI dated | Limited advanced modeling, scaling cost | Limited collaboration, no version control |
| Pricing (approx.) | ~$19.60/month (Individual); perpetual from $98–$294 depending on license | Free, Pro starts at $9/user/month | Enterprise ($29.99 per month) and non-commercial ($16.99 per month) plans are available |
| Learning Curve | Manageable | Low | Moderate |
DbSchema
Best for
- SMBs and developers that need a visual tool that supports multiple database types.
- Managing both SQL and NoSQL databases.
Key Features
- Visual database design with drag-and-drop schema designer.
- Support for reverse engineering databases into diagrams.
- HTML5 documentation generator for schema sharing.
- Schema synchronization with update script generation.
- Git support for version control and team collaboration.
- Relational data editor supporting offline data editing.
- Supports many databases, including SQL Server, MySQL, PostgreSQL, MongoDB, and Cassandra.
Pros
- Simple to use; design chores require little SQL.
- Sturdy cross-platform and multi-database support.
- Allows schema synchronization and offline editing.
- Reasonably priced for SMB spending plans.
- Effective documentation tools improve collaboration within the team.
- Runs on Windows, macOS, and Linux.
Cons/Limitations
- Absence of native cloud data warehouse integration.
- The user interface could seem outdated in comparison to cloud-native technologies.
Pricing
- Free trial available.
- Pricing starts at ~ $29 for a monthly developer plan. An individual perpetual license will cost $294 (plus taxes), and if you want to provide access for a team, you will need to pay $730 (plus taxes).
- Commercial licenses and team subscriptions are available.
Learning Curve
- Relatively “gentle” learning curve; suitable for users with basic database knowledge.
- Good online tutorials and documentation.
Lucidchart
Best for
- SMBs and agile teams that need cloud-based, flexible diagramming with data modeling capabilities.
- Combining data modeling with flowcharts, org charts, and general diagramming.
- Real-time collaboration across remote locations.
Key Features
- Cloud-based visual diagramming with extensive ERD shapes and templates.
- Import/export database schemas (SQL import wizard).
- AI-assisted diagram generation and editing.
- Broad diagram palette covering workflow and process visualization.
- Integrations with Google Workspace, Microsoft 365, Slack, and Atlassian.
Pros
- Minimal setup, effortless to use.
- No installation required.
- Real-time collaboration with commenting and sharing.
- Fast update cadence with new AI features baked in.
- Clear visuals that business users can read and build.
Cons/Limitations
- Less focused solely on database modeling vs. specialized tools.
- Some advanced data modeling features may be limited.
- Pricing scales for team collaboration and advanced features.
Pricing
- A free tier with limited functionality is available.
- Pro plans start at $9 per user per month.
- An enterprise plan is offered on a custom basis.
Learning Curve
- Suitable for beginners and mixed-technical teams.
Navicat Data Modeler

Best for
- SMBs and developers who need affordable yet strong data modeling.
- Working with multiple database types, including MySQL, PostgreSQL, Oracle, MariaDB, SQLite, SQL Server, and Snowflake.
- And everyone who seeks complete conceptual, logical, and physical data modeling.
Key Features
- Database structure visual design that supports IDEF1X, UML, and Crow’s Foot notations.
- Using SQL/DDL generation for both forward and reverse engineering.
- Converting models between various database types.
- Integration with cloud-based databases as well as other database platforms.
- Without creating SQL scripts, users can model tables, views, functions, and procedures.
Pros
- Reasonably priced in contrast to expensive enterprise technologies.
- Support for various DBMSs is effective in a wide range of settings.
- Strong modeling capabilities and an easy-to-use UI.
- Good on-premises and cloud database support.
- Internet-based materials and a vibrant user base.
- Runs on Windows, macOS, and Linux.
Cons/Limitations
- Limited advanced collaboration features compared to other tools on this list.
- The UI may feel dated in comparison to newer cloud-based apps.
- No built-in version control is available; manual coordination is required.
Pricing
- The tool offers two plans: one for enterprises and another for non-commercial organizations.
- Individual perpetual licenses for enterprises are $399 per user, and for non-commercial use, the price is $329.
- Monthly and annual subscription options are also available. For enterprises, the prices are $29.99 and $299.99, and for non-commercial use, the prices are $16.99 and $169.99, respectively.
- 14-day fully functional free trial.
Learning Curve
- Moderate.
- The tool is suitable for users with some experience in databases or modeling.
Best Free & Open-Source Tools
| Aspect | Oracle SQL Developer Data Modeler | MySQL Workbench | pgModeler |
|---|---|---|---|
| Best for | Oracle DB developers | MySQL/MariaDB developers | PostgreSQL developers |
| Key Features | Multi-model, engineering, integration | Modeling, SQL, migration | Visual design, forward/reverse engineering |
| Pros | Free, rich features, Oracle integrated | Free, cross-platform, all-in-one | Open-source, PostgreSQL-focused |
| Cons | Oracle-centric, complexity | Limited to MySQL, UI lags | PostgreSQL-only, fewer features |
| Pricing | Free | Free | Free (~$25 binaries) |
| Learning Curve | Moderate to steep | Moderate | Moderate |
Oracle SQL Developer Data Modeler
Best for
- Organizations that are deeply invested in Oracle-centric environments but also need support for other ecosystems.
- Create logical, relational, and multidimensional models.
Key Features
- Supports conceptual, logical, relational, and multidimensional modeling.
- Forward and reverse engineering with Oracle and other DBMS.
- Integrated with Oracle SQL Developer for smooth database management.
- Data type and constraint management.
- Collaboration with version control and model comparison.
- Auto-generation of DDL scripts and detailed visualizations.
Pros
- Simplifies complex data structures with intuitive visualizations.
- Rich diagramming and visualization capabilities.
- Supports multiple modeling paradigms.
- Operates on Windows, macOS, and Linux.
Cons/Limitations
- Tuned mainly for Oracle; coverage for other engines is thinner.
- Steep for newcomers; concepts can overwhelm at first.
- Smaller community than popular open-source modelers.
Pricing
- Completely free; part of the Oracle SQL Developer suite.
Learning Curve
- Somewhere between moderate and steep due to feature richness and integration maturity.
- Extensive official documentation and tutorials will contribute to learning the product.
MySQL Workbench
Best for
- MySQL and MariaDB developers who require modeling, SQL development, and server administration.
- Small to medium projects focused on MySQL databases.
Key Features
- Visual database design with forward/reverse engineering.
- SQL editor with syntax highlighting.
- Performance dashboards and reporting.
- Migration tools from other DBMS.
- Schema synchronization and documentation tools.
Pros
- Open-source and totally free.
- Cross-platform, including Linux, macOS, and Windows.
- Integrates database development and maintenance with modeling.
- Powerful community backing.
Cons/Limitations
- Primarily MySQL/MariaDB focused.
- UI may be less responsive with large schemas.
- Lacks advanced collaboration/version control features.
Pricing
- Free (GPL license).
Learning Curve
- Moderate, aimed at developers and DBAs.
- Extensive documentation and community forums will significantly ease the onboarding process.
pgModeler (Open-Source)
Best for
- PostgreSQL developers who need a dedicated open-source modeling tool.
- Small to medium teams focused on PostgreSQL.
Key Features
- Visual drag-and-drop schema design.
- Forward and reverse engineering for PostgreSQL.
- SQL code generation with PostgreSQL-specific features (partitioning, inheritance).
- Multi-platform support (Windows, macOS, Linux).
Pros
- Free and open-source.
- PostgreSQL specialized in full feature support.
- Simple, clean UI.
- Supports custom datatypes and constraints.
Cons/Limitations
- Limited to PostgreSQL.
- Lacks enterprise-grade collaboration features.
- Smaller user base.
Pricing
- Free (source code).
- Compiled binaries available for ~$25 for convenience.
Learning Curve
- Moderate, requires basic PostgreSQL knowledge.
- Good community support and documentation will help to get through the introduction stage, and in case of bottlenecks.
Best Niche & Specialized Tools
| Aspect | Hackolade |
|---|---|
| Best for | NoSQL-focused modeling teams, polyglot database environments |
| Key features | Visual modeling, polyglot support, reverse/forward engineering, CI/CD integration, collaboration, robust documentation |
| Pros | Specialized for NoSQL, intuitive UI, broad DB support |
| Cons | Subscription cost, smaller community, may be overkill for purely relational needs |
| Pricing | Free trial, $132/seat/month subscription, community edition available |
| Learning curve | Moderate, with good guidance and resources |
Hackolade
Best for
- Data architects focused on JSON, XML, and schema-based data governance.
- Organizations and developers working with NoSQL databases and polyglot data environments.
- Designing, managing, and governing schemas across both SQL and NoSQL databases and APIs.
Key Features
- Visual data modeling for NoSQL, SQL, and storage formats, including JSON and XML Schema.
- Support for reverse engineering of live databases to create models.
- Forward engineering with schema generation.
- Collaboration tools with version control and concurrent modeling.
- Automated model validation, comparison, and merging.
- Integration with CI/CD pipelines for DevOps workflows.
- Strong data dictionary and documentation generation capabilities.
- Polyglot support across relational, document, key-value, and graph databases.
Pros
- It has an intuitive user interface that will satisfy both technical and business users.
- The ability to model multiple database types using only one tool.
- Constant updates with new collaborative and schema governance features.
- Cloud-based and desktop implementation options, including a browser-based UI with no installation required.
Cons/Limitations
- Advanced features and team collaboration are unlocked only in paid tiers.
- Comparatively smaller user community than legacy tools like erwin or ER/Studio.
Pricing
- Free 14-day evaluation with full features (no credit card needed).
- Monthly subscription at about $132 per seat/month for the professional edition.
- Community edition with limited features available for free.
Learning Curve
- Moderate; designed to be user-friendly with a focus on visual modeling.
- Extensive documentation, webinars, and tutorials are available.
- Suitable for users familiar with database concepts but new to NoSQL modeling.
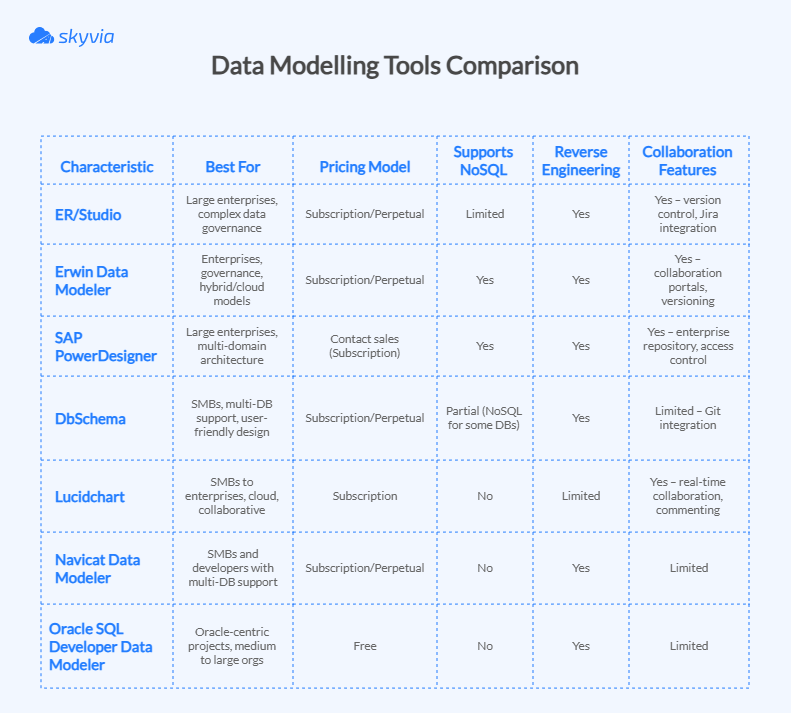
At-a-Glance: Feature Comparison Table
By now, your brain is probably buzzing with all the names, pros, cons, and limits we’ve discussed. Here is a concise table to help you summarize everything mentioned above.
How to Choose the Right Data Modeling Tool for Your Project
Picking a modeling tool isn’t just shopping for features. It’s matching your data reality with the least friction and the most future.
Measure twice, cut once, then automate the cut.
1. Assess Your Database Environment
Start with the lay of the land – the database or databases you’re managing. However, it’s important to recognize possible future shifts if they are already visible on the horizon.
Not all modeling tools are compatible with every database. Some are monogamists, while others are more like polyglots. If you’re on MySQL or PostgreSQL, most tools will feel native. Running NoSQL or multi-model, too? Tools like Hackolade specialize in that.
Note: It’s best when a tool can handle the usual suspects plus, potentially, cloud heavyweights like Snowflake and Redshift.
2. Consider Your Team Size and Collaboration Needs
Working solo? Lucky you – one less aspect to consider. Working on a team? Still lucky you – all those tasks and responsibilities will be distributed among many. Yet, beforehand, you need to think about how everyone’s going to play together in the modeling sandbox.
If you co-edit in real time, want change tracking, and need safe branching, tools with multi-user collaboration and version control are the best match.
Git integration or a built-in repo will keep architects, DBAs, and stakeholders on the same page, even on the same paragraph, instead of burning working chats.
3. Evaluate by Business Size
Small teams and startups should focus on tools that won’t require selling a DBA’s kidney. Free tools and affordable perpetual licenses are your friends.
You don’t need enterprise bells and whistles; instead, you need something lean that works, doesn’t cost a fortune, and won’t require a PhD to operate.
If you’re playing in the big leagues, the list of features you can’t ignore becomes longer. You’ll need strong collaboration features, data lineage tracking, and enough governance capabilities.
4. Match Features to Your Primary Use Case
Your primary mission should drive your tool selection.
If you’re modernizing legacy systems, reverse engineering is your MVP to pull live schemas into clean models and run impact analysis.
Designing cloud-native from scratch? You’ll want forward engineering for one-click DDL and smooth integration with platforms like Redshift or Snowflake. Bonus points for tight links to catalogs and DevOps so metadata stays in lockstep.
5. Balance Your Budget vs. Long-Term Value
The final price always stretches beyond licensing. Quite often, training, support, and the time you’ll save with automation and docs you can trust are given little or no consideration at all. Summarize every investment, whether it’s someone’s time or money, to understand the actual price.
Subscription vs perpetual is a business call, but future-proofing matters either way. Favor vendors with an active roadmap, scalability for growing data, and flexibility for polyglot persistence as your stack grows.
6. Utilize Free Trials
Never marry the first demo. Run a pilot with real models, real people, and real success criteria: modeling accuracy, delivery speed, user satisfaction, and governance fit.
Pull in DBAs, developers, architects, and business users; bring everyone who will have to work with the tool in the future. A week of tire-kicking now beats months of buyer’s remorse later.
Putting Your Model to Work: Integrating with a Data Platform Like Skyvia

A data model is the blueprint. But blueprints don’t build houses. You need a construction crew that knows how to read the plans and make them a reality – a data integration tool like Skyvia.
It’s a match made in heaven. One shows what to build; the other gets concrete poured and steel bolted, so your analytics don’t wobble when the first-time guests ring the doorbell.
Models define entities, keys, and rules; integration runs the playbook at scale. Skyvia slots in and reads the plan, lines up sources and targets, enforces the rules you set, and keeps everyone on schedule.
Once your structure is signed off, use Skyvia Import to populate it with data from 200+ sources into your target warehouse or database. Mapping respects your model’s datatypes and constraints, while transforms handle the nitty-gritty – splits, merges, lookups, and surrogate keys.
Your data model will (not might) change over time. Business requirements and regulations shift, new data sources are being added, and the model must respond accordingly.
In the old days, it would be marathon-long updates with fingers crossed that nothing would break and bring you back to the start line. With Skyvia, you can update mappings instead of rewiring scripts.
- Synchronization keeps systems in step with incremental loads and conflict rules.
- Replication can snapshot whole objects to match your physical model, then switch to incremental loads so you don’t pay the tax on complete refreshes.
- Data Flow handles multi-step transforms.
- Control Flow orchestrates retries, branches, and schedules so overnight runs don’t turn into all-nighters.
Ready to turn diagrams into dependable pipelines? Start a free trial of Skyvia Integration and put your model to work today.
Conclusion
There isn’t a single “best” data modeling tool, but out there, you can find the right fit for your scale, budget, stack, and guardrails, which is much better than a unified solution can ever be.
Small teams often win with simple UX and low cost. Bigger players lean on governance, lineage, and rock-solid collaboration. Your choice should mirror your workloads and the way your team works and delivers.
Final advice
- Start with requirements – scope, target DBMS, model levels, governance must-haves.
- Use the comparison table to build a 3–5 tool shortlist mapped to must-have features.
- Pressure-test with free trials and a real model: run forward/reverse engineering, docs, and versioning.
- Define what can be declared a success in your case – accuracy, delivery speed, onboarding time, and TCO.
- Involve everyone in this “shopping” process so the tool fits day-to-day reality, not just the demo.
Select the tool that keeps your schemas clean, your documents accurate, and your delivery on schedule. And Skyvia will help you to populate your models.
F.A.Q. for Data Modelling Tools
Can data modeling tools be used for reverse engineering existing databases?
Yes! Tools like MySQL Workbench, pgModeler, erwin, and ER/Studio import live schemas to diagrams for documentation and impact analysis.
What is the difference between ER/Studio and erwin?
Both are enterprise-grade. erwin leans into governance/catalog and lineage; ER/Studio is praised for large-model performance, naming standards, and Team Server collaboration. UX and pricing differ.
Which data modeling tool is best for NoSQL databases like MongoDB?
Hackolade is the standout. DbSchema also supports MongoDB well. Look for JSON schema handling, nested structures, and forward/reverse engineering.
How does a data model help with data integration?
It’s the contract: entities, keys, types, and rules. ETL/ELT maps to it, reducing errors, standardizing data, and validating lineage/governance so systems sync cleanly and analytics stay trustworthy.