When teams in your organization function in different environments, the natural question arises: how to establish a smooth handshake? For example, you run customer profiles in PostgreSQL, sales in MySQL, and logistics tracking in Oracle. Now picture this multiplying across every business unit, across different databases and systems, with reports lagging and decisions delayed.
The database-to-database integration can take away the pain. It’s about making your disparate databases communicate with each other, allowing data to flow smoothly instead of getting stuck in silos. You gain insights faster, reduce duplicate work, and make informed decisions with the complete picture.
Table of Contents
- What is Database-to-Database Integration?
- Common Use Cases for Database-to-Database Integration
- Why is Database Integration a Strategic Imperative?
- Methods of Database Integration
- Choosing the Right Database Integration Tool
- How Skyvia Handles Real-Life Database-to-Database Integration Cases
- Conclusion & Final Thoughts
What is Database-to-Database Integration?
Database-to-database integration is the process of connecting and sharing information between two or more databases to synchronize data across them. Integration is a bridge that allows data to flow between systems, ensuring all functions and teams are up to speed.
It doesn’t matter if your data is housed in the cloud, like Amazon RDS, in-house servers running SQL Server, or anything else. It does not even matter if your data is on multiple systems. The solution is on the plate!
Key Concepts
- Data Synchronization
With data synchronization integration keeps your data consistent across databases, either real-time (instant updates) or batch mode (scheduled updates).
Real-time example: A global e-commerce company updates inventory levels across its EU, US, and APAC databases just after a purchase happens online. The stock count reflects reality, no matter where the customer is located.
Batch example: A hospital collects patient data across multiple clinics and updates its central reporting database every night. Time isn’t critical here, but the accuracy by the next morning is.
- Data Consolidation
When your purpose is not just syncing, but the consolidation of data from multiple databases into a single source of truth, integration is a central hub where everyone works with consistent data.
Example: A financial services company consolidates customer transactions from Oracle, risk analysis from PostgreSQL, and compliance records from SQL Server into a single analytics warehouse. Decision-makers no longer waste time reconciling multiple reports.
- Data Transformation
Different databases often “speak” in various formats. Data transformation makes sure the data is reshaped, cleaned, and enriched as it moves between systems.
Example: A logistics company receives shipment records in Oracle with “MM-DD-YYYY” date format and delivery logs in PostgreSQL with “YYYY-MM-DD.” Transformation ensures both systems align before reports are generated.
- Integration Environments
Integration isn’t limited to a single setup. It can happen between:
- On-premises databases (for example, Oracle or SQL Server).
- Cloud databases (like Snowflake, BigQuery, or PostgreSQL on AWS).
- Hybrid models, where companies use both local and cloud environments.
Database-to-database integration involves connecting, syncing, and preparing data so that it’s no longer scattered and inconsistent.
Common Use Cases for Database-to-Database Integration
Below, we have collected the most common scenarios that involve integrating databases.
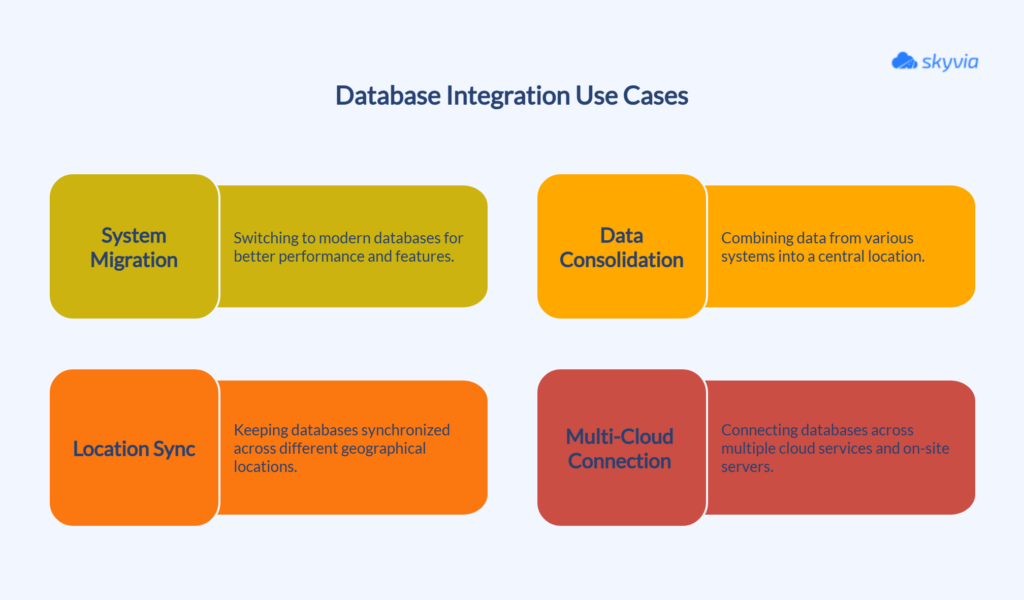
Migrating from Obsolete Systems to Modern Ones
Many organizations switch from outdated databases to modern ones to unlock faster performance, real-time analytics, and access to new and innovative features.
This process involves data format conversion and adaptation to new structures, while ensuring the business continues to operate smoothly.
Data Consolidation
Putting data from CRM systems, ERP tools, and other business apps into one central location helps you see the whole picture. This way, you get a complete view of your customers and operations, making it easier to take wise decisions.
Sync Across Locations
When your teams are spread across cities or countries, syncing databases ensures everyone’s working with the latest information. This makes collaboration smooth and keeps your data accurate, no matter where people are.
Connecting Databases in Multi-Cloud and Hybrid Setups
These days, it’s common to have databases in several cloud services or split between cloud and on-site servers. Integration allows data to flow easily, regardless of its location, ensuring everything works together seamlessly.
Why is Database Integration a Strategic Imperative?
When information is distributed across multiple systems and services, the first task of business is just to not get lost and to generate meaningful insights for decision-making as fast as possible and with minimum effort.
Thus, data integration is a tactical enabler of decision-making, operational activity, and sustained growth. Let’s look at it in more detail.
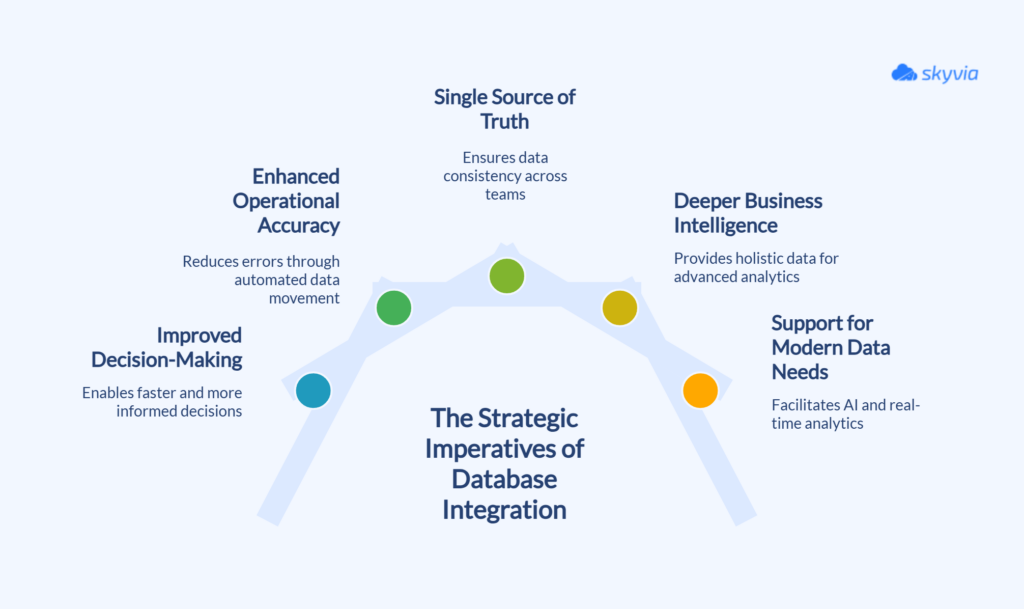
Improved Decision-Making
When databases collaborate, leaders no longer have to rely on stale reports or fragmented dashboards. Real-time data flows enable organizations to act more quickly and base their decisions on up-to-date information.
Enhanced Operational Accuracy
Manual processes are slow and error-prone. Integration replaces repetitive tasks with automated flows. That eliminates mistakes and helps to avoid constant ball passing between teams.
A Single Source of Truth
Conflicting numbers across departments are a common pain point. Integration aligns data across all systems and creates consistency.
Everyone works from the same version of the truth, which builds trust in the numbers and makes collaboration much easier.
Deeper Business Intelligence
By bringing together different datasets, the integration forms an all-around view of the information. Analytics teams can go beyond surface-level reports and delve into in-depth analysis that drives strategy.
Support for Modern Data Needs
Initiatives such as predictive analytics, AI, and machine learning rely on large, unified datasets. If data is siloed, these projects stall.
Integration ensures the foundation is in place so businesses can actually tap into advanced technologies rather than talk about them in theory.
Methods of Database Integration
There are several approaches you can use to integrate databases. The best approach for your case depends on the business needs, the volume, and the speed at which the updates are required. Below are the primary techniques implemented by enterprises:
API-based Integration
Modern APIs support REST and GraphQL protocols, providing efficient and real-time data retrieval. You can build a custom app that works via API. This offers flexibility and full control over the integration.
Pros: Highly controlled, flexible, secure data access.
Cons: Rate-limited or vendor-limited, may require high costs for development and maintenance resources.
Best for: Real-time integration with diverse or cloud-based systems. Suitable for enterprises that have the resources on development and maintenance.
Database Replication Techniques
Databases provide the classical solutions for data exchange.
ETL / ELT
ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) involves data extraction from a source, transformation to match the target database structure, and loading to target.
The main feature of ELT (Extract, Load, Transform) is that the transformation is done after loading, through the target database’s compute resources.
Pros: Proven, reliable, handles very large amounts of data well.
Cons: Not ideal for real-time updates, and configuration can be complex.
Best for: Data warehousing projects, where businesses need historical data to analyze.
CDC
CDC (Change Data Capture) tracks changes to a source database (inserts, updates, deletes) and replicates them in near real time to the target database.
Pros: Synchronizes databases virtually in a blink, minimizes unnecessary data transfer.
Cons: More complex to configure, might require database-native features.
Best for: use cases where up-to-the-minute accuracy matters. For example, syncing financial transactions or product inventory across channels.
Middleware Solutions
Middleware platforms, such as Skyvia, Informatica, Hevodata, or others, facilitate database-to-database integration as an intermediate layer that enables communication, data exchange, and translation between databases and systems.
Middleware platforms help with data format conversion, protocol translation, routing, and transformation. Thus, databases with different interfaces or data structures can communicate with one another effectively without the need to modify the underlying databases or applications.
Pros: flexibility, security, scalability, legacy systems integration, and complex workflows support.
Cons: advanced scenarios may be more expensive, and may require complex initial setup.
Best for: Organizations that deal with complex integration scenarios and those who are looking for reliable and secure solutions without assigning dedicated resources for development.
Choosing the Right Database Integration Tool
With all these tools and means utilized, the question is no longer whether you can or cannot integrate databases, but what means is best for your business.
The “right” tool will be determined based upon your company size, data strategy, and plans. Below are the key considerations to keep in mind.
Pre-Built Connectors
It should have pre-configured connectors for highly used databases, such as MySQL, PostgreSQL, Oracle, and SQL Server, as well as modern cloud systems like Snowflake or BigQuery. This reduces setup time, enabling you to focus on integration without having to build connections from scratch.
No-Code/Low-Code Interface
Not every company maintains a pool of developers in reserve. A no-code or low-code interface enables business users and analysts to model integration flows using visual tools rather than scripts. This continues the projects moving at a fast pace without halting activity on IT resources.
Data Quality and Transformation Capabilities
A good tool offers built-in transformations, data type conversions, cleansing, and enrichment, ensuring that the data that reaches the destination database is ready for use.
Scalability and Performance
As the volume of data grows, so should your integration platform. Look for tools that can handle millions of records, scale across multiple environments, and perform during peak workloads.
Security and Compliance
Data integration involves handling sensitive data, such as customer, financial, or health information. Products must provide encryption, secure authentication, and compliance features to meet regulations such as GDPR, HIPAA, or SOC 2.
How Skyvia Handles Real-Life Database-to-Database Integration Cases
The market offers a great variety of data integration tools, and Skyvia is the one that consolidates all these features into a single platform.
It is a versatile platform that helps businesses handle complex integration scenarios without heavy coding or infrastructure headaches.
Skyvia offers:
- An extensive range of database, cloud application, and storage system connectors.
- A visual, no-code integration flow designer.
- Sophisticated transformations.
- Cloud scalability without the need for setup infrastructure.
- Enhanced security features to protect data.
Here are several examples of how Skyvia tools can solve real-life integration challenges.
Oleksandr Khirnyi, Chief Product Officer at Skyvia said: “The launch of the Automation product represents a significant advancement in our mission to optimize data-related processes and help businesses achieve greater results with minimal effort. With a user-friendly visual designer, intuitive logic creation, and automatic error detection, we empower organizations to automate complex operations while reducing manual involvement.”
Migrating from Obsolete Systems to Modern Ones
When companies move from outdated databases to modern platforms, it often means dealing with schema changes, data type mismatches, and ongoing business operations that can’t pause. Skyvia handles these challenges easily in a few clicks without coding and technical expertise.
- Skyvia Import tool offers advanced Data Mapping tools that help to align completely different structures with new ones.
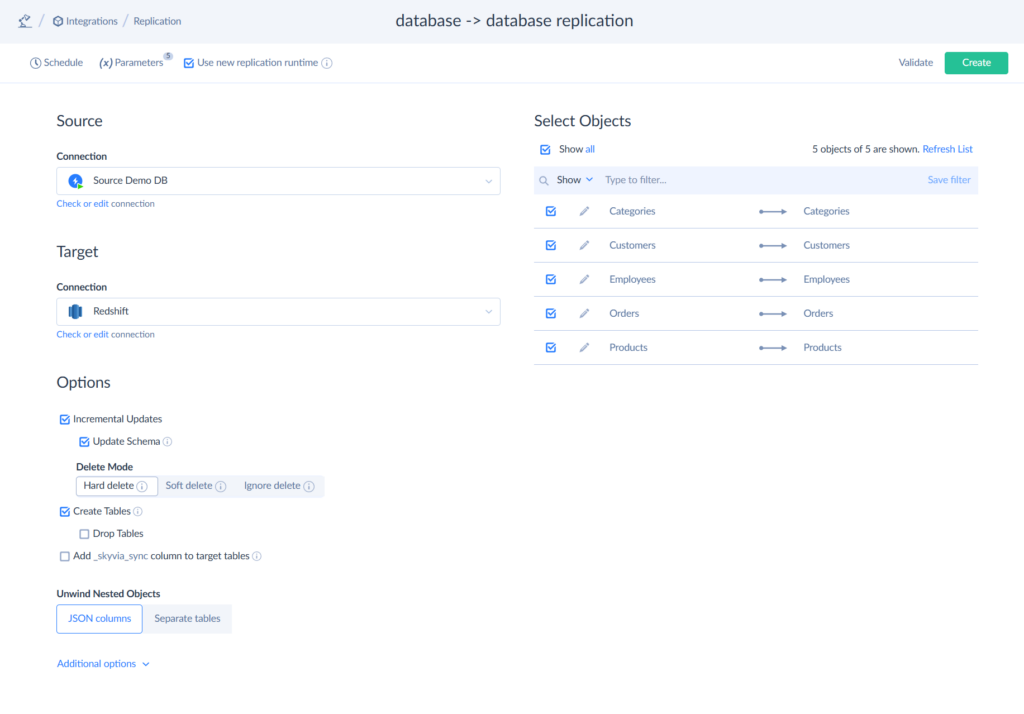
- Skyvia Replication with Incremental Updates enables the constant data transfer, keeping systems online throughout the process. It provides smooth migrations, with preserved data integrity, and no disruptions.
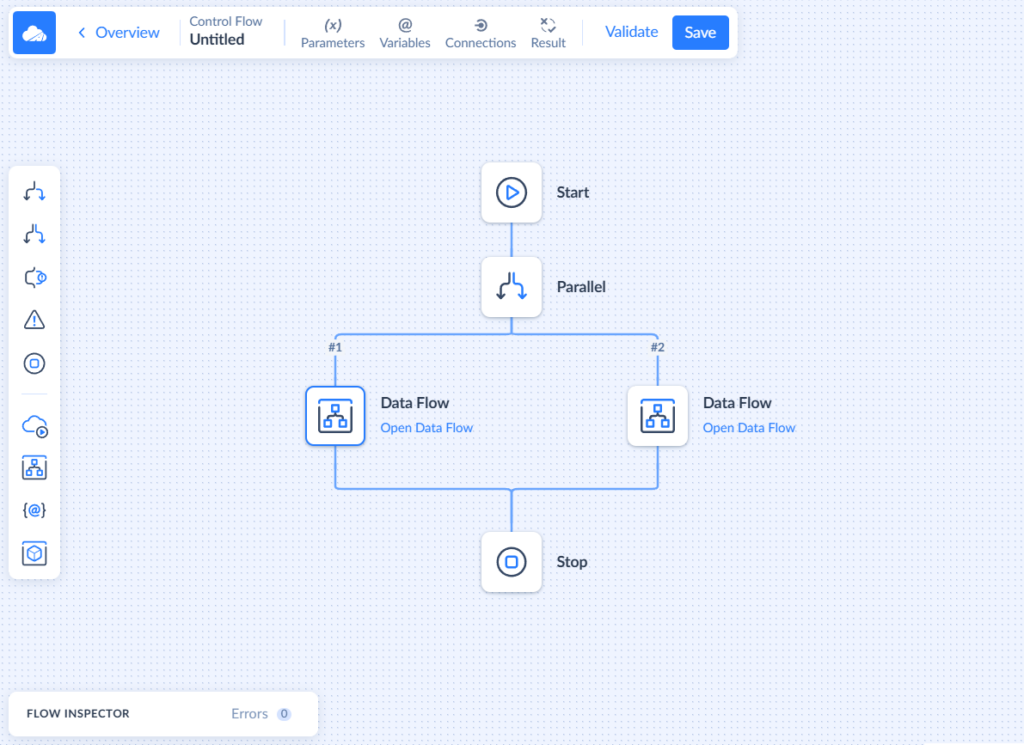
Data Consolidation
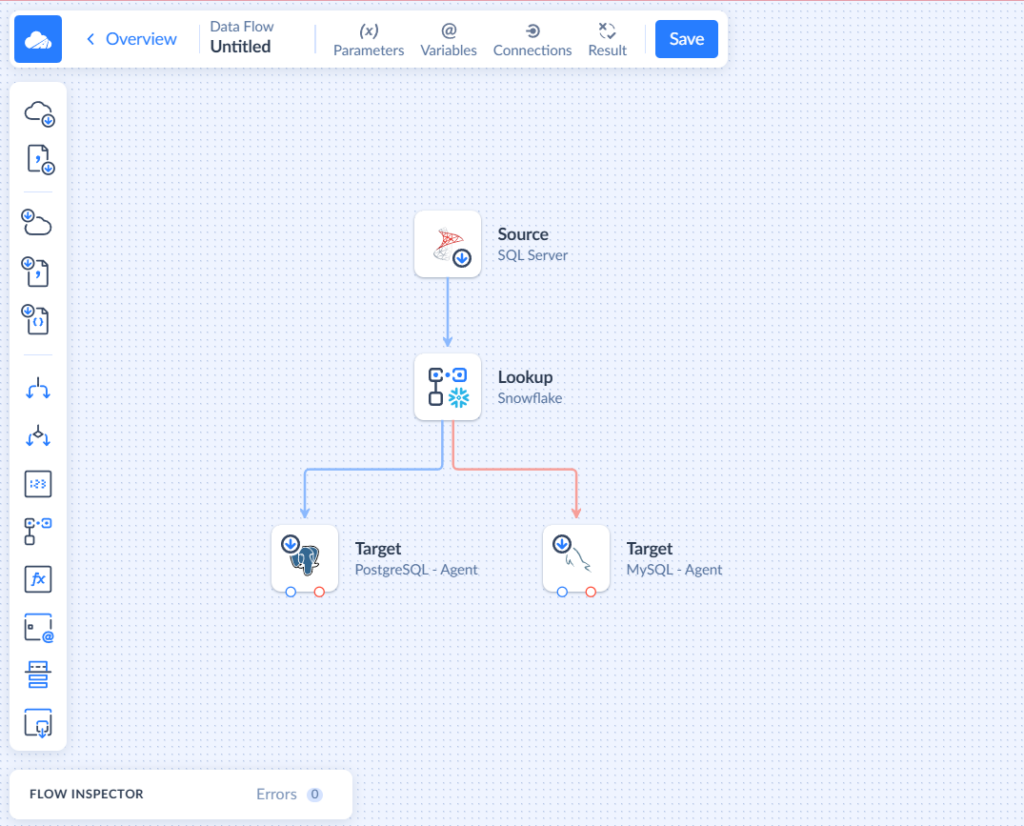
Skyvia offers a solution to the problem for gathering data scattered across multiple sources in one place. With Data Flow and Control Flow, you can implement almost any scenario using a friendly drag-n-drop interface.
- Combine data from multiple sources
- Perform complex multistage transformations
- Design data flows visually, on a convenient diagram
Sync Across Locations
Global companies often need to keep branch offices aligned. Skyvia makes this possible with Synchronization tool. That way, teams across countries always work with the same, accurate information, which strengthens collaboration and keeps operations aligned.
- Two-way synchronization so changes in one database instantly appear in another.
- Conflict resolution rules to ensure data consistency.
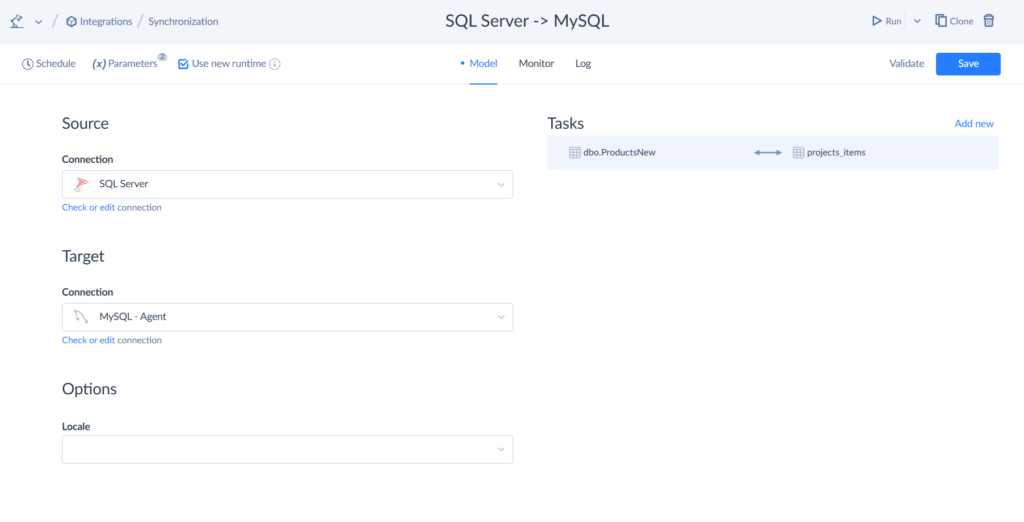
Connecting Databases in Multi-Cloud and Hybrid Setups
Businesses rarely stick to just one environment. Many combine cloud apps with on-premises systems. Skyvia is designed for this reality, offering:
- Cloud-to-cloud and cloud-to-on-premises integration.
- Scalable infrastructure that grows as data volumes expand.
- Scheduled integration.
Conclusion & Final Thoughts
Database-to-database integration grew from an afterthought in technology to a business necessity. With information scattered across CRMs, ERPs, cloud offerings, and on-premises infrastructure, organizations that fail to integrate risk slower decision-making, redundant work, and lost opportunities.
The good news is that modern-day integration tools have streamlined it. Something that took massive IT personnel and custom-made scripts previously can now be done by merely looking at it, with automated flows and pre-built connectors.
If the need is migrating away from legacy systems, converging data for analytics, synchronizing geographically dispersed teams, or integrating hybrid environments, integration ensures data becomes an asset and not a bottleneck.
In the future, there will be a greater need for real-time data, AI, and predictive analytics. Those firms that lay a solid database foundation today will be far better positioned to take advantage of these trends in the future.
If your business is facing these challenges, Skyvia has found a secure, scalable, and flexible way to make integration worthwhile without heavy lifting. Start with a free trial, test your scenarios, and find out how quickly you can connect the dots.
F.A.Q. for Database-to-Database Integration
Can I integrate databases from different vendors, like Oracle and SQL Server?
Yes, integrating databases from different vendors is possible using tools that support cross-platform connectivity, such as JDBC or ODBC drivers, facilitating data synchronization between systems like Oracle and SQL Server.
What is the most common method for database integration?
The most common method is ETL (Extract, Transform, Load), which involves extracting data from various sources, transforming it into a usable format, and loading it into a target system, such as a data warehouse.
How does database integration support business intelligence (BI)?
Database integration consolidates data from diverse sources, ensuring consistency and accuracy, which is crucial for BI tools to perform reliable analysis and generate actionable insights.
How do I ensure data security during the integration process?
Implementing encryption for data at rest and in transit, using secure access controls, and conducting regular audits are essential practices to maintain data security during integration processes.


