Over 150,000 organizations use Salesforce to keep customer records, sales pipelines, and other business-critical information. This data is a treasure for any business. At the same time, it attracts hostile gold miners, competitors, and intruders craving sensitive information. That’s why each company must act to protect its Salesforce organizational account.
To help you with that, we’ve prepared a Salesforce security guide. In it, you’ll learn Salesforce security best practices for safeguarding data.
Table of Contents
- Basics in Salesforce Security
- 10 Salesforce Security Best Practices For Your Business
- The Role of Skyvia in Salesforce Data Security Best Practices
- A Continuous Journey of Salesforce Security
- Wrapping Up
Basics in Salesforce Security
Cloud data has always been vulnerable to cyberattacks and intruder invasions. However, employees could also contribute to insider Salesforce data leaks and integrity violations. To address potential threats in Salesforce, take a look at the core components of Salesforce security first:
- Authorization outlines the permissions for data access and system configuration for each user based on their profile.
- Visibility determines which data a user can view and manipulate. At the organization-wide level, there are three visibility levels:
- Public Read/Write. All users can view and edit all data.
- Public Read Only. All users can view all data. Only content owners can edit data.
- Private. Content owners can view and edit only their data.
- Sharing rules provide access to users depending on the record type, content owner, etc.
- Authentication verifies the user’s identity before logging into the system. Salesforce supports standard username-password access type, multi-factor authentication (MFA), and single sign-on (SSO).
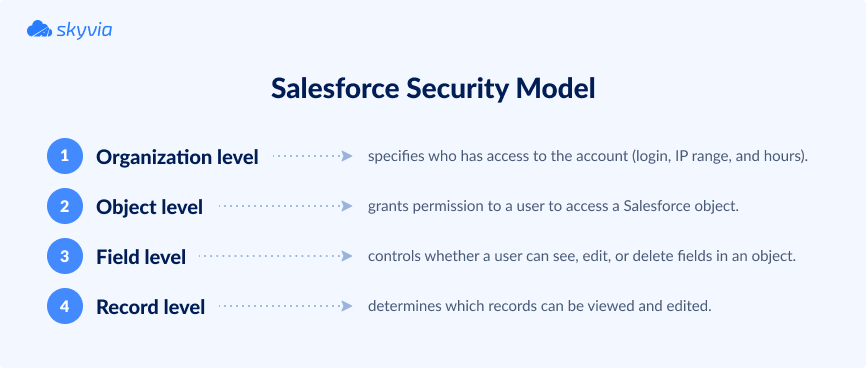
As for data protection, Salesforce adapts a four-tier security model:
- Organization level specifies who has access to the Salesforce organizational account by setting the login IP range and hours.
- Object level grants permission to a user to access a Salesforce object.
- Field level controls whether a user can see, edit, or delete fields in an object.
- Record level determines which records in an object can be viewed and edited by which users (depending on their profile).
Understanding the basics of the Salesforce security model helps to take the necessary measures to protect organizational data from internal and external threats. You may decide who needs access to which information, what restrictions to set, etc.
10 Salesforce Security Best Practices For Your Business
1. Enable Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
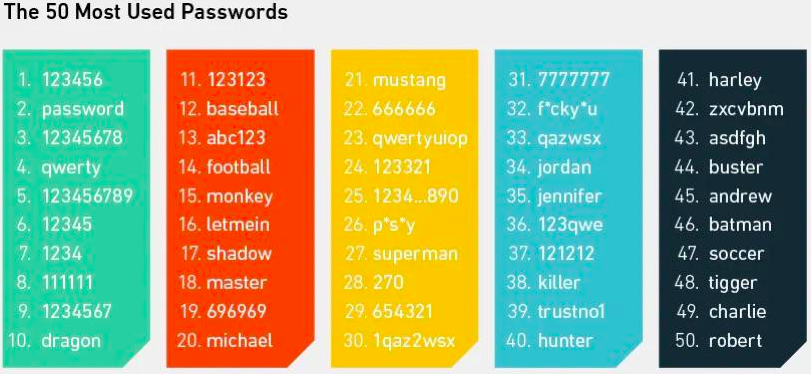
Username and password credentials are commonly used across the web to access accounts. However, this approach isn’t secure enough because modern hackers quickly discover secret combinations. Check the most popular passwords and avoid using them for organizational accounts.
An MFA approach was invented to grant better login security. It implies a two-step login: first, a user enters their credentials; then, a user confirms the login action on their personal smartphone.
2. Restrict access by using IP ranges
Set access to a Salesforce account only from the trusted IP range (corporate network or VPN). Users logging into Salesforce from external IP addresses must verify their identity.
3. Apply granular access control using profiles and permission sets
In 2024, Salesforce implemented enhanced permissions that have entirely redesigned data-sharing habits. They grant granular access control via four access levels to documents:
- Full Access provides the right to share, edit, and delete a document. It also allows a user to change sharing settings by adding or removing thread members, editing access levels, and adding or removing folders.
- Can Edit permission enables users to edit a document, view sharing links, and check collaborators.
- Can Comment allows users to see link sharing and edit history, send new messages and requests for editing, and leave comments.
- Can View allows users to view link sharing and send new edit requests.
4. Establish secure password management policies
Many online services specify a list of password requirements for user account creation. Salesforce isn’t an exception: it requires a password to be at least eight characters long and contain digits and characters. Salesforce also sets a security question on user registration.
Experts recommend using at least a 15-character password for a Salesforce user account. So, encourage your employees to establish strong passwords for their Salesforce accounts. Administrators can use Workbench for Salesforce to force reset weak passwords.
5. Run checks on your organization’s security status
Use the built-in Health Check procedure to identify any white spots in current security settings. It calculates the organization’s security score based on the Salesforce Baseline Standard index.
Organizations requiring extra security levels may consider creating a custom baseline. It allows administrators to specify the number of login attempts, password complexity, etc.
6. Evaluate the use of Salesforce Shield
Another way to advance security is the Salesforce Shield solution. It can be of great value to governmental, healthcare, and financial organizations.
Salesforce Shield comprises three security tools for building extra levels of protection:
- Shield Platform Encryption helps to encrypt Salesforce fields containing sensitive data and protect it from unauthorized access. It also ensures that your data corresponds to external and internal compliance policies.
- Real-time Event Monitoring provides detailed information about performance, security, and usage data. It shows who accesses business-critical data at what time and where.
- Field Audit Trail ensures that you’re aware of the value and state of Salesforce data.
Another tool, Einstein Data Detect, scans your data, identifies sensitive information, and recommends measures to protect it.
7. Carry out regular audits
Salesforce auditing features provide information about system use, revealing potential security issues. They don’t secure a user account from existing threats but keep you on the right track in safeguarding organizational data.
To make sure the system is secure, pay attention to the following usage trends during auditing:
- Login history.
- Record modification fields.
- Setup audit trail showing logs with modifications on organizational Salesforce account configuration.
8. Beware of phishing emails
Phishing emails look very real and seem to come from a legitimate organization, but they don’t. Their primary purpose is to steal confidential information (usernames, passwords, and credit card details).
Phishers may send emails with a malicious link from force.com domain, for example. To recognize and timely detect malicious intents of phishing emails, check whether it asks you one of the following:
- Click a link
- Open an attachment
- Log in to your account
- Validate password
If any of these options are present, it’s most likely a phishing email. In such a case, you must report suspicious activity to the Salesforce Security team at security@salesforce.com.
At the same time, Salesforce recommends taking the following actions to decrease the risk of phishing emails:
- Ensure that MFA is implemented for all Salesforce user accounts.
- Activate IP range restrictions to allow users to access Salesforce only from the corporate network or VPN.
- Inform your employees about what phishing emails usually look like and instruct them not to open suspicious emails.
- Use tools for advanced protection that tend to block phishing emails.
- Implementing DMARC and DKIM authentication to prevent unauthorized senders from spoofing your domain.
9. Ensure connection security
Another best practice implies secure HTTPS connections with any third-party domain. For that, proceed with the following steps:
- Click on the cog icon and go to Setup in your Salesforce organizational account.
- In the search box, find Session Settings and click on it.
- Select Require secure connections (HTTPS) for all third-party domains.
10. Make regular backups
The backup and recovery strategy is among the best practices for preserving Salesforce organizational data. Decide which data needs to be backed up and how often it needs to be backed up. Then, in case of unexpected data corruption or hacker attacks, you can restore data anytime.
The Role of Skyvia in Salesforce Data Security Best Practices
Salesforce has native data backup and recovery solutions, but they are rather conventional. That’s why Salesforce encourages users to consider third-party solutions with a more comprehensive approach and set of features for backup and recovery.
To help you implement Salesforce data security best practices, we’d like to introduce Skyvia. This is a universal cloud data platform containing the following products:
- Data Integration
- Query
- Backup
- Automation
- Connect
Here, we’d like to focus on the Backup product, enhancing the security of Salesforce data.
Skyvia Backup is designed to back up data from supported cloud applications either automatically on a schedule or manually. This tool helps you organize your Salesforce data backups according to the planned schedule.
Skyvia Backup allows you to select data, such as sensitive information or anything you prefer. The backed-up data can then be viewed, exported, or restored directly to a data source on demand. All these operations are done via a user-friendly Skyvia interface in a web browser.
It’s important to note that Skyvia stores the backed-up data in an encrypted form on a secure Azure environment. Moreover, our tool uses a unique encryption key for each user, so no one except a user doesn’t have any access to the backed-up data.
Skyvia Backup can be used absolutely for free if the total amount of the backed-up data doesn’t exceed 1 GB. Once more storage space is required, you may switch to the paid solutions at affordable prices.
A Continuous Journey of Salesforce Security
Monitor the most recent trends and regulations on Salesforce Security’s official website. There, you’ll find news related to security and announcements on webinars with expert recommendations.
If you want to explore security enhancement practices deeply, we recommend referring to the official Salesforce security guide. It contains all the security-related aspects and explains how to implement them.
Wrapping Up
Salesforce data has always been attractive to parties with malicious intentions. Therefore, it’s necessary to implement the best practices for Salesforce security within your organization.
Multi-factor authorization, strong passwords, granular access control, and regular audits often enhance Salesforce accounts’ internal security. When data needs to travel outside of Salesforce, Skyvia protects it by offering secured channels for data transfer and safe backup solutions.