Running a business today without solid data integration is like trying to run a restaurant with the kitchen, bar, and waitstaff all using different menus. Orders get mixed, timing’s off, and no one’s quite sure what’s happening.
That’s what happens when the systems don’t talk to each other. You end up with siloed data, delayed insights, and teams working harder just to stay afloat.
Proper data integration solves that while pulling all the info together. From sales to support, to supply chain, into a single, streamlined flow.
The result? Smarter decisions, fewer errors, and a business that runs like it’s actually on the same page.
A strong data integration strategy is mission-critical for:
- Scaling operations.
- Improving customer experience.
- Gaining real-time insights that drive growth.
In this article, we’ll break down the key components of data integration that make successful data integration possible, like:
- ETL.
- Mapping
- Synchronization.
- Cleansing.
- Replication.
- Federation.
Each one plays a vital role, and knowing how they work together helps people build a system that’s flexible, efficient, and ready to grow with your business.
Table of Contents
- What is Data Integration?
- Why is Data Integration Important for Businesses?
- Key Components of Data Integration
- Data Integration Challenges
- Best Practices for Data Integration
- Conclusion
What is Data Integration?
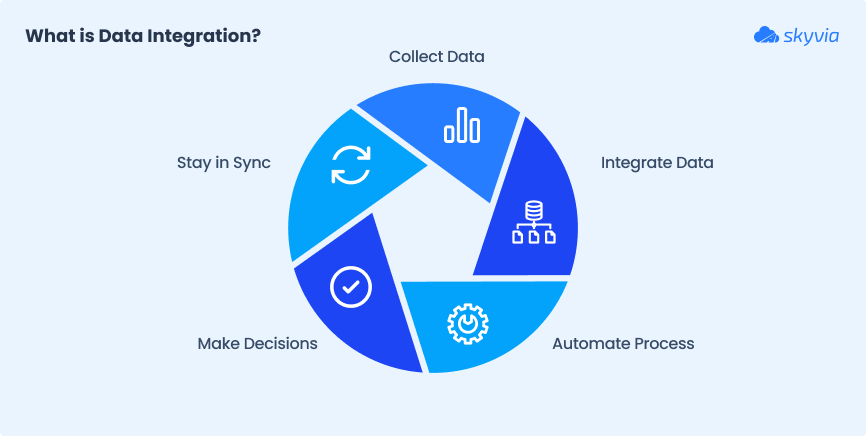
It’s the process of combining data from multiple sources into a single, unified view. So teams can actually use it to
- Make decisions.
- Automate workflows.
- Stay in sync.
In other words, it’s how your CRM talks to the ERP, how marketing shares insights with sales, and how you finally stop exporting five spreadsheets to get one report.
Originally, this was all done manually. Think copy-pasting CSVs, merging databases by hand, and crossing your fingers that nothing broke.
Today, we’ve got modern tools that do the heavy lifting automatically, in real-time, and without all the duct tape.
A good data integration setup connects the apps, databases, cloud platforms, and analytics tools so the right info flows where it’s needed instantly and accurately.
Real-world example
Innovium experience
Problem
Inovium, a consulting firm, was juggling data across tools like HubSpot, QuickBooks, Jira, and Confluence. Nothing was connected. Reporting was a nightmare, project profitability was hard to track, and every decision felt like guessing in the dark.
Fix
Instead of hiring a dev team or piecing together a patchwork of scripts, they turned to Skyvia. With its no-code setup, they linked everything into a single SQL Server database in just a few clicks. No custom code. No headaches.
Result
All the data now made sense. Their team could track project health, reporting became smooth, and developers time was saved.
Why is Data Integration Important for Businesses?
Picture this: marketing, sales, finance, and support systems all working in isolation, and everyone drowning in different data versions. That chaos slows collaboration, drains time, and clouds decision-making.
Data integration unifies information across systems so businesses run on accurate, timely insights.
Here’s how it boosts value:
- Faster, smarter decisions. Centralized data means quicker report generation and rapid response to market shifts.
- Operational efficiency. Automated workflows eliminate manual data entry and reduce errors.
- Better customer experience. A 360° customers’ interactions lets companies personalize interactions and respond faster.
- Competitive edge. Streamlined data supports innovation and helps users stay ahead of the curve.
Real Outcomes
AHCA (American Health Care Association) experience
Problem
The American Health Care Association moved from an on-prem SQL Server to Dynamics 365 but still needed SSRS reports from their old setup.
They faced the challenge of keeping both systems aligned without disrupting reporting functions.
Fix
They used Skyvia to build data pipelines that incrementally mirrored Dynamics 365 data back into their on-premises SQL Server without rewiring existing systems, just steady, automated replication.
Result
Accurate, up-to-date reports streamed automatically; no manual intervention, no delays. The team regained peace of mind and refocused on data insights.
Ātman Consultants experience
Problem
Ātman had to unify data from ERP, Pipedrive, Klaviyo, and Onfleet for Fiji retailers. Manual syncing was slow, error-prone, and siloed teams internally.
Fix
With Skyvia, they created real-time data pipelines that updated ERP and synced key records (customer, order, delivery) across platforms, automated and in sync.
Result
Sales teams got real-time order info in Pipedrive, marketing flowed automatically via Klaviyo, logistics synced instantly with Onfleet, and manual entry became a thing of the past.
Key Components of Data Integration
There are a few core building blocks you’ll see in any solid setup:
- ETL.
- Mapping.
- Synchronization.
- Cleansing.
- Replication
- Federation.
Different tools, like Skyvia, Talend, Fivetran, and Zapier, handle these tasks in various ways.
Let’s break down what each piece does and why your data will thank you later.
ETL (Extract, Transform, Load)
It’s the classic way to move data: grab it from one place, clean it up, and drop it where it needs to go.
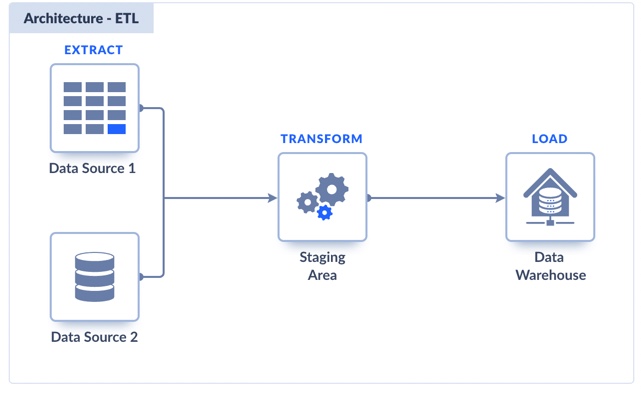
Think of it like moving apartments, but with spreadsheets instead of sofas.
- Extract: Pull data from your source (a database, a cloud app, wherever).
- Transform: Fix the weird date formats, rename the columns, and drop the junk.
- Load: Push the clean, usable data into the destination system.
Platforms like Stitch, Talend, and Fivetran handle some flavors of ETL.
However, Skyvia makes it easy to build full pipelines without code. You can schedule jobs, apply filters and lookups, and move data between dozens of sources, all in one place.
Data Mapping
This process is like introducing two systems that don’t speak the same language. You need to ensure “First Name” over here ends up in the right box over there, not in “Company Name” or something weird.
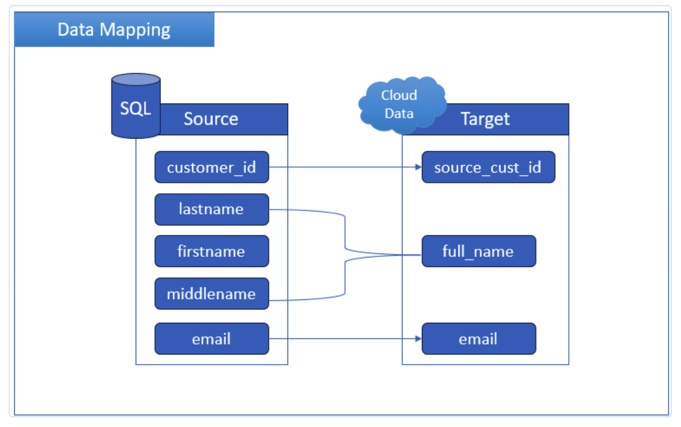
It’s the behind-the-scenes translator that keeps the data from turning into a mess.
- Match fields from source to destination.
- Reformat content as needed (dates, currencies, etc.).
- Handle custom fields, lookups, and naming mismatches.
Often, tools like Talend or Informatica offer basic field mapping or require custom scripts. Skyvia keeps it visual and flexible. Just drag, drop, and tweak formulas, and you’re done.
Data Synchronization
Data sync is like keeping two playlists updated on different apps. Changing something in one should update the other.
Without it, things drift, and you end up working with old info or duplicate records.
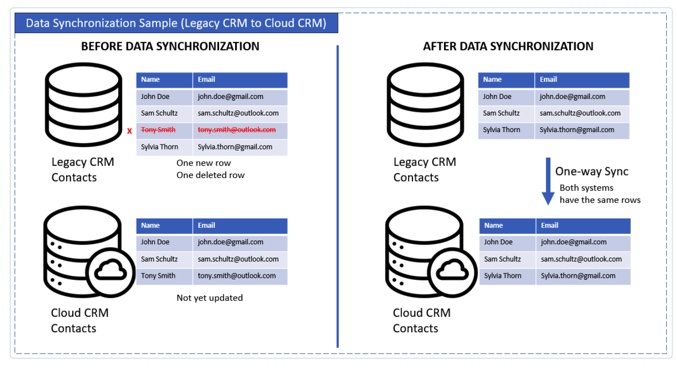
This approach ensures that all the systems are communicating with each other, not just exchanging awkward hellos.
- Keeps data consistent between systems.
- Works in one direction or both.
- Can run in real time or on a schedule.
Some platforms (like Dell Boomi or Zapier) offer sync tools, but they’re often one-way or limited to specific triggers.
Skyvia handles both one-way and two-way synchronization, automatically tracks changes, and allows users to run syncs as often as needed, with no manual push required.
Data Cleansing
It’s like cleaning out the contacts list. You delete duplicates, fix weird formatting, and finally get rid of that one entry that just says “???”
Skipping this step ends up importing chaos into the systems and leading to terrible business decisions.
- Removes duplicates, blanks, and bad entries.
- Fixes format inconsistencies (dates, phone numbers, etc.).
- Standardizes values so systems can understand each other.
Tools like OpenRefine or Talend offer dedicated cleansing features, often with a steep learning curve.
Skyvia integrates cleansing directly into the process: use filters, expressions, lookups, and conditional logic to clean data as it is being imported. No separate tool or cleanup phase is required.
Data Replication
This step keeps a fresh copy of your data elsewhere, allowing users to query it, report on it, or sleep better at night.
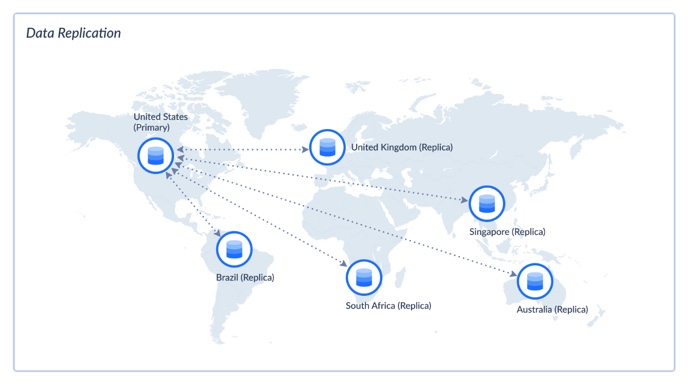
- Copies data from source to destination.
- Can run on a schedule (hourly, daily, etc.).
- Supports full loads or just the changes (incremental).
Systems like Fivetran, Hevo, or Stitch focus on replicating data into warehouses, mostly for analytics. But they often come with stricter source limitations or require SQL to fine-tune.
Skyvia, on the other hand, supports replication from a wide range of cloud apps like Salesforce, HubSpot, and Zendesk into relational databases with automatic schema creation, change tracking, and no coding needed.
Want to see it in action?
Watch this tutorial on replicating Zoho Desk data with Skyvia.
Data Federation
This approach provides access to multiple sources. You query data where it lives: no copying, no syncing, no storage drama.
- Allows users to pull data from multiple sources in real time.
- No need to move or replicate data.
- Great for dashboards, monitoring, or when systems need to stay separate.
Solutions like Denodo or Dremio are built for enterprise-level federation but come with steep setups and learning curves.
Skyvia keeps it lightweight with Skyvia Query, allowing you to run SQL queries across cloud apps and databases directly from the browser or expose them via OData if needed.
Data Integration Challenges
Bringing data together sounds great until you run into
- Systems that don’t talk.
- Formats that don’t match.
- Rules that don’t budge.
Integration isn’t just a tech puzzle; it’s a business one too.
Here are some of the most common roadblocks and tips on how to navigate them without losing your mind (or data).
System Compatibility
Some platforms play nice. Others act like they’ve never heard of each other.
- Problem. Different data models, APIs, or tech stacks that don’t connect easily.
- Fix. Use integration tools with wide connector support and flexible mapping.
- Risk. Manual workarounds, broken syncs, or missing data in key reports.
Tip: Before choosing tools, audit your data sources and see which platforms offer native or no-code connectors.
Poor Data Quality
Bad data means bad insights out. If the inputs are messy, the results will be too.
- Problem. Duplicates, missing values, and inconsistent formats.
- Fix. Build cleansing into your integration flows using filters, validations, and standardization rules.
- Risk. Reports that don’t match reality, misinformed decisions, wasted time.
Tip: Don’t wait to clean data after it’s loaded. Apply filters, rules, and validation steps before integration to keep junk from spreading across your systems.
Data Silos
Each department has its own tools, data, and way of naming “customer.”
- Problem. Data is scattered across tools that don’t share easily.
- Fix. Use integration to centralize or sync key data into shared systems.
- Risk. Missed insights, duplicated effort, no single source of truth.
Tip: Start by identifying overlapping data across departments. Then integrate around shared fields like customer ID or email to break silos without forcing a full rebuild.
Security & Compliance
Integrating data across systems means moving and exposing sensitive info. That’s a big deal.
- Problem. Risk of data leaks, breaches, or non-compliance with GDPR, HIPAA, etc.
- Fix. Encrypt in transit, use role-based access, and choose tools that support compliance frameworks.
- Risk. Fines, reputational damage, and legal headaches.
Tip: Choose tools with built-in encryption, audit logs, and role-based access. And always check if they support the compliance standards your industry actually cares about.
Latency & Timing Issues
Sync too slowly, and the reports are outdated. Sync too often, and you overload the systems.
- Problem. Data updates lag behind, or systems get stressed.
- Fix. Use smart scheduling or incremental updates to balance freshness and performance.
- Risk. Teams working off stale info or dealing with sync errors.
Tip: Not all data needs to sync in real time. Prioritize freshness where it matters (like inventory) and schedule the rest to avoid unnecessary load.
Governance & Ownership
Who owns the data? Who cleans it? Who breaks it when the field name changes?
- Problem. No clear ownership of data pipelines or definitions.
- Fix. Establish data governance policies and assign responsibility.
- Risk. Confusion, finger-pointing, and unpredictable results.
Tip: Assign a data owner for every major source or flow. When everyone knows who’s responsible, issues get fixed faster, and finger-pointing gets replaced with accountability.
Best Practices for Data Integration
The best integrations are invisible. They just work. Getting there means clear goals, clean data, smart automation, and solid communication between people.
Here’s what works.
Start with a Clear Strategy
Don’t just plug systems together and hope for the best.
- Define your goals (reporting, syncing, or migration).
- Know your sources and destinations.
- Document what “done” looks like.
A well-scoped integration plan avoids scope creep, missed fields, and messy data halfway through the project.
Focus on Data Quality and Governance
Good integration starts with clean data. Garbage in, garbage multiplied.
- Run validations and cleansing before syncing.
- Standardize formats, fix mismatches, remove duplicates.
- Assign data owners and enforce naming rules.
Don’t wait to fix quality problems after your reports break. Bake it into your process.
Use Automation Where It Makes Sense
Manual syncing is a trap. It’s slow, error-prone, and easy to break.
- Schedule regular jobs.
- Use change tracking or triggers for incremental syncs.
- Let no-code platforms handle repeatable flows.
Automation frees your team up to focus on logic, not logistics.
Keep Business and IT Aligned
Integration isn’t just a technical problem. It’s a cross-team project.
- Involve business users to define what’s important.
- Let IT design for scale, performance, and security.
- Use shared language (not just tech jargon).
No one wants to sync “customer data” only to find out they meant completely different fields.
Test Early & Monitor Always
Assume something will break. You just want to catch it before it matters.
- Run test syncs in sandbox environments.
- Monitor job success/failure logs.
- Validate outputs against expected results.
The goal is visibility. Know what changed, when, and why.
Conclusion
Data integration isn’t just a backend task. It’s the backbone of modern business operations.
From syncing systems to cleaning data, each part of the process plays a key role in keeping information accurate, accessible, and ready for action.
We’ve covered what makes data integration work.
- The key processes behind it.
- The common roadblocks to watch out for.
- The best practices that make it all run smoothly.
You may merge tools, automate workflows, or build a real-time reporting setup. In all these cases, smart data integration keeps everything running smoothly behind the scenes.
Ready to make your data flow better?

F.A.Q, for Components of Data Integration
Do I need coding skills to set up data integration components?
Not always. Many platforms, such as Skyvia, Zapier, and Workato, offer no-code tools to build pipelines, map fields, and automate data flows without requiring scripts.
How often should data integration components be updated?
Update schedules depend on the data and use case. Some syncs run hourly or daily, while others require real-time updates for live systems.
How do I ensure data security in integration components?
Use tools that offer encryption, access controls, and compliance support. Monitor integrations and limit access to sensitive data.
Which tools are best for managing data integration components?
Skyvia, Talend, Fivetran, and Informatica are popular choices, each offering different features for ETL, sync, automation, and governance.
How long does it take to set up data integration components?
It depends on complexity. Simple syncs can take minutes with no-code tools. Larger multi-system setups may take days or weeks to configure and test.

