Trying to understand the customers with scattered data is like trying to read a book with half the pages missing. You can guess the storyline, but you’ll always be off.
When all the pieces of customer info come together, the plot finally makes sense. You know who your customers are, what they want, and how to keep them coming back.
The problem? Most businesses don’t have that complete book. Customer data is split across CRMs, marketing automation tools, e-commerce platforms, support systems, etc. Each platform tells part of the story, but never the whole thing. The result: teams making decisions with blind spots, and customers feeling like they’re talking to strangers instead of a company that “gets” them.
That’s where Customer Data Integration (CDI) gives users a hand. Think of it as stitching all those torn pages back together into one clear, reliable book. CDI creates a single source of truth for customer data, accessible, accurate, and actionable.
In this article, we’ll walk through 12 best practices for CDI. Step by step, you’ll see how to build a stronger customer data strategy, avoid common pitfalls, and finally give your business the superpower of truly knowing the customers.
Table of contents
- What is Customer Data Integration (CDI)?
- Why CDI is a Non-Negotiable for Modern Businesses
- The Customer Data Integration Process: A Step-by-Step Framework
- 12 Customer Data Integration Best Practicces
- Common CDI Tools and Technologies
- Conclusion
What is Customer Data Integration (CDI)?
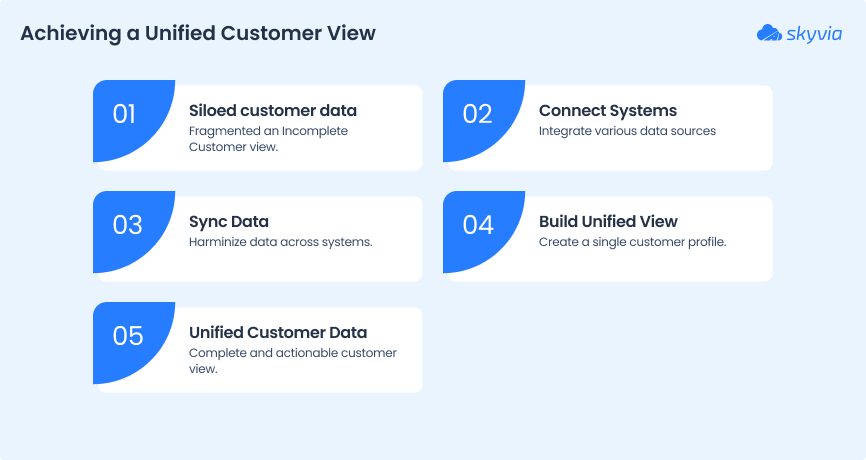
It’s about consolidating customer information from different systems into a single, unified story to view. Instead of juggling scattered data in CRMs, e-commerce apps, support platforms, and marketing tools, CDI may bring it all together in one reliable place.
Think of it like: without CDI, any business is flipping between dozens of half-finished notebooks, trying to guess the story. With CDI, you finally have one clean book where every chapter is in order.
Customer data comes in many shapes.
Like here:
- Demographic. Names, emails, job titles, locations.
- Transactional. Purchases, invoices, renewals.
- Behavioral. Clicks, app usage, website visits.
- Qualitative. Survey responses, reviews, support conversations.
When these live in silos, you’re left with blind spots. CDI stitches them together, giving every team (sales, marketing, and support) the same reliable customer view.
And the best part? You don’t need a team of engineers to get there. With a no-code integration platform like Skyvia, Zapier, or Integrate.io, businesses can connect systems, sync data, and build that unified customer view without writing scripts.
So, you obtain a single source of truth that’s not just technically possible, but practically usable.
Why CDI is a Non-Negotiable for Modern Businesses
Now the businesses run on data like the city runs on subways. If the trains aren’t connected, people get stuck. Same with customer data. If it’s scattered, everything slows down. When you integrate it, things start moving.
Here’s why CDI isn’t optional for everyone:
Enhanced Customer Experience
- Unified data means you can treat customers like people, not puzzle pieces. Think Amazon-style “you might also like” recommendations or Spotify’s custom playlists. Every touchpoint feels tailored, not generic.
Improved Marketing ROI
- With CDI, marketing teams stop shooting in the dark. Imagine sending ads only to customers who actually fit the profile, like retargeting abandoned carts on Shopify. The budget stretches further because every campaign is sharper.
Increased Sales Opportunities
- A complete view reveals patterns you’d miss otherwise. For example, if someone bought running shoes, CDI helps flag the chance to upsell them socks or a fitness app. Cross-sells and upsells stop being guesswork.
Data-Driven Decision Making
- CDI turns messy exports into a clear dashboard. A retailer, for instance, can see which products drive repeat purchases and adjust inventory before stockouts happen. Decisions become proactive, not reactive.
Improved Data Governance & Compliance
- Having one reliable source of truth makes audits and compliance less of a nightmare. Instead of chasing records across apps, everything is centralized, making GDPR or CCPA requests easier and safer to handle.
The Customer Data Integration Process: A Step-by-Step Framework
Building a solid CDI process isn’t rocket science. It’s more like setting up a good subway map. You need to know where the stations are, how the trains connect, and who’s monitoring the system so it doesn’t break down. Here’s the step-by-step:
Step 1: Define Your CDI Goals and Objectives
Before you start wiring systems together, you need a game plan. Are you trying to improve customer experience? Boost marketing ROI? Simplify compliance? Set the “why” first; otherwise, you’re just moving data around with no finish line.
Step 2: Identify and Map Your Data Sources
Customer data hides in more places than pigeons in the park. CRMs, e-commerce platforms, marketing tools, support systems, and billing apps. The list goes on. Map out every touchpoint so you know where the streams start before you connect them.
Step 3: Extract, Transform, and Load (ETL)
This is the plumbing. You extract the data from each source, transform it so the formats and fields match, then load it into a central place. ETL tools like Skyvia, Fivetran, or Airbyte do the heavy lifting, so you don’t have to hand-code every pipe.
Step 4: Data Cleansing and Standardization
Raw data is messy, like handwritten notes on a crumpled napkin. Cleansing fixes typos, standardizes formats (think phone numbers or addresses), and removes duplicates. Without this step, your “single source of truth” ends up as a single source of noise.
Step 5: Load into a Centralized Repository
Once the data is clean, it needs a home. That could be a data warehouse (like Snowflake, BigQuery, or Redshift) or a Customer Data Platform (CDP). This is your central library where every department checks out the same book, not their own mismatched copies.
Step 6: Ongoing Monitoring and Maintenance
CDI isn’t a one-and-done job. It’s like garden maintenance in the park. Data flows change, APIs update, and new systems get added. Set up monitoring, alerts, and regular reviews to keep pipelines healthy and reliable.
12 Customer Data Integration Best Practices
Here’s the truth: CDI isn’t a “set it and forget it” project. It’s more like keeping the park clean. If you want people to enjoy it, you’ve got to take care of it. These best practices help companies build a CDI approach that’s strong, scalable, and actually useful for each business.
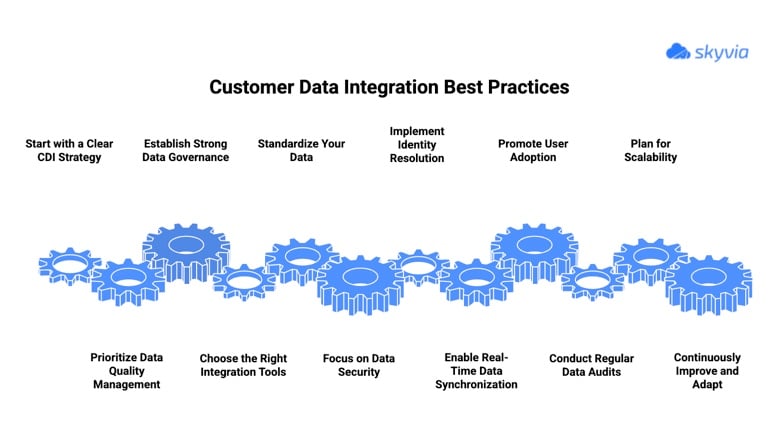
1. Start with a Clear CDI Strategy
Don’t wire systems together just because you can. Define what success looks like, whether it’s personalized marketing, faster reporting, or better compliance, and align those CDI goals with your overall business objectives.
2. Prioritize Data Quality Management
Garbage in, garbage out. Set up rules for cleansing, validating, and enriching data before it hits your warehouse. Think of it as cleaning your shoes before stepping onto the picnic blanket.
3. Establish Strong Data Governance
Someone needs to own the rules. Define roles, responsibilities, and standards for data management so everyone knows who’s responsible for keeping things consistent and compliant.
4. Choose the Right Integration Tools
Pick tools that fit your team’s skills and needs. ETL platforms, CDPs, and iPaaS solutions all have their place. No-code platforms like Skyvia shine here. They make CDI accessible without needing an engineering army.
5. Standardize Your Data
Ensure fields and formats line up across systems. A “phone number” should look the same whether it comes from Salesforce, Shopify, or HubSpot. Standardization keeps the puzzle pieces fitting together.
6. Focus on Data Security
Customer data is valuable and vulnerable. Use encryption, access controls, and compliance frameworks (like GDPR and CCPA) to protect sensitive information. Trust is easy to lose, hard to rebuild.
7. Implement Identity Resolution
The same customer might show up three times in your systems. Different emails, same person. Identity resolution merges duplicates into a single record, giving one accurate profile per customer.
8. Enable Real-Time or Near-Real-Time Data Synchronization
Customers don’t live in batch mode, and neither should the data. Keep systems synced so updates flow instantly, like stock changes from the ERP hitting your e-commerce storefront without delay.
9. Promote User Adoption
Even the cleanest data is useless if no one uses it. Train teams on how to access and apply integrated data. The more people see its value, the more it becomes part of daily decision-making.
10. Conduct Regular Data Audits
Check your pipelines regularly. Are the right fields still mapping? Is the data fresh and complete? Audits help you catch issues early, before they snowball into costly mistakes.
11. Plan for Scalability
The data volumes will grow. It’s not a maybe; it’s a given. Choose a CDI solution that scales with your business instead of breaking when you double your customers or add new systems.
12. Continuously Improve and Adapt
Customer data needs will evolve, and so should the CDI strategy. Add new sources, refine processes, and stay flexible. Think of it as ongoing park maintenance. You don’t just mow once and call it done.
Common CDI Tools and Technologies
Customer Data Integration isn’t one-size-fits-all. Different tools play different roles. Some handle the plumbing (ETL), some build a central hub (CDPs), others connect apps with no code (iPaaS), and some enforce a single golden record (MDM). Think of it like a toolkit: you pick the wrench, screwdriver, or hammer depending on the job.
ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) Tools
ETL pipeline tools are the workhorses of data integration. They pull data out of source systems, clean and reshape it, then load it into a central warehouse. This is the classic approach for turning raw, scattered inputs into analysis-ready tables.
- Example: Skyvia’s ETL makes it easy to extract Shopify orders, transform them into the right format, and push them into Snowflake or SQL Server. No manual scripts needed.
Customer Data Platforms (CDPs)
CDPs specialize in creating a persistent, unified customer database. They collect, clean, and organize customer data into profiles that can be used across marketing, sales, and service. Think of them as customer-centric warehouses.
- Example: A marketing team could use a CDP to unify demographics from Salesforce, behavior from Google Analytics, and purchases from Shopify, then launch targeted campaigns based on the complete profile.
iPaaS (Integration Platform as a Service)
iPaaS tools are like universal adapters. They connect cloud apps and databases without coding, letting businesses sync customer data automatically. This is where Skyvia really shines:
- Redmond Inc. used Skyvia iPaaS to automate Shopify-to-ERP order syncs and feed Power BI dashboards, saving $60K annually.
- Cirrus Insight integrated QuickBooks, NetSuite, and Salesforce via Skyvia, cutting integration costs by 20×.
Master Data Management (MDM) Tools
MDM focuses on creating a “single source of truth” by standardizing and mastering customer records. It ensures that “John A. Smith” in CRM and “Jonathan Smith” in billing are recognized as the same customer. MDM tools are critical in large enterprises with massive, overlapping datasets.
- Example: Skyvia’s MDM capabilities allow businesses to easily extract customer data from various systems, resolve duplicate records, and merge them into a central repository. This method ensures that “John A. Smith” in CRM and “Jonathan Smith” in billing are recognized as the same customer, without any manual intervention.
Conclusion
So, CDI isn’t just a nice-to-have. It’s the backbone of any business that wants to stay competitive. From connecting any customer data across systems to creating a single source of truth, a strong CDI strategy drives better customer experiences, improved marketing ROI, and smarter business decisions.
It’s like putting together the ultimate puzzle: once all the pieces are in place, you can finally see the big picture clearly. And that’s where Skyvia becomes a good choice.
With this no-code data integration platform, you can easily:
- Connect all the systems you use.
- Automate workflows.
- Build the unified customer view.
Ready to take the next step? Try Skyvia’s free trial today or schedule a personalized demo.
F.A.Q. for Customer Data Integration
How long does it take to implement a CDI strategy?
Implementation time depends on complexity, but with tools like Skyvia, Zapier, and Fivetran, basic integrations can take a few hours or days. Larger, more complex setups may take a few weeks to configure and align all systems and processes.
What are the main challenges of customer data integration?
Common challenges include data quality issues, managing duplicate records, ensuring data security, and achieving real-time synchronization across systems. No-code tools like Skyvia help streamline these tasks and simplify integration.
How does a CDP differ from a CRM?
A CDP aggregates customer data from multiple sources to create unified profiles, while a CRM focuses on managing customer interactions and relationships. A CDP is more data-centric, while a CRM is interaction-focused.

