Your sales data lives in the CRM. Inventory’s locked in the ERP. Marketing’s got its own spreadsheet jungle.
Finance? They’re running reports from a system nobody else touches.
It’s the classic data silo problem, where every team’s flying with their own version of the truth, and getting a complete picture means endless copy-paste, CSV exports, and “Can you send me that file?” emails.
Data centralization changes the game.
Instead of chasing data across tools, you bring it all into one secure, connected hub. A single source of truth that every team can trust, update, and actually use in real time.
In this article, you’ll learn:
- What data centralization actually is and what it isn’t (no, it’s not just “storing everything in one database”).
- Why it’s a game-changer for decision-making, collaboration, and growth.
- How to build a centralization strategy step by step without breaking your existing workflows.
- The common pitfalls companies face (and how to avoid them before they get expensive).
- Best practices for keeping your centralized data accurate, secure, and useful.
- Where the future’s headed and why flexible data lakehouses are becoming the next big thing.
Table of Contents
- What is Data Centralization?
- How to Implement a Data Centralization Strategy: A Step-by-Step Guide
- Common Challenges of Data Centralization and How to Overcome Them
- Best Practices for Sustainable Data Centralization
- The Future of Data: The Rise of the Flexible Data Lakehouse
- Conclusion
What is Data Centralization?
It’s the process of gathering data from scattered sources, like CRMs, ERPs, ad platforms, spreadsheets, and bringing it all into one secure, unified repository. This approach becomes the go-to place for accurate, consistent, and up-to-date insights across each business.
Think of data as books spread across different branches, where finding one answer means a scavenger hunt.
Centralization is like building a centralized library catalog. All the books are registered and easy to find in one place. Everyone just browses. No guessing. No wasted time.
Centralization vs. Decentralization
- Centralization. One source of truth. Easy access, governance, and consistency. Everyone refers to the same data.
- Decentralization. Data lives separately in different systems. It leads to confusion, duplicates, and decisions based on outdated or mismatched info.
Business Example
- Pain. An e-commerce client had billing data scattered across QuickBooks, PayPal, and Stripe, confusing Sales, Marketing, and AR teams.
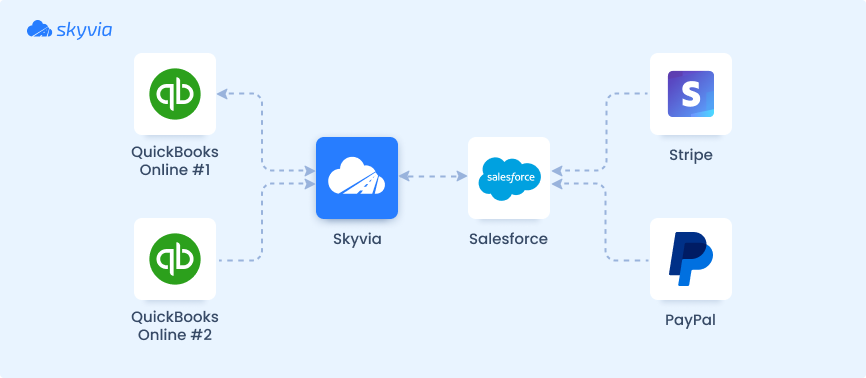
- Solution. They used the Skyvia data integration platform that consolidated billing data into Salesforce, giving every team instant visibility into customer and payment details.
Why It Matters: The Data Explosion
The scale of data is exploding. In 2025 alone, the world is on track to generate around 181 zettabytes of data, up over 23% year-over-year. That’s about 2.5 quintillion bytes per day, 29 terabytes every second.
This isn’t future tech hype. It’s today. And if your data isn’t centralized, that volume makes chaos inevitable.
Why Data Centralization is a Game-Changer for Your Business
Centralizing data isn’t just a technical upgrade but a strategic advantage. Here’s why businesses that do it well pull ahead.
1. Enhanced Decision-Making
When everyone works from a single source of truth, decision-making stops being guesswork. Leaders see the same real-time metrics, not outdated reports or conflicting numbers.
Example. Project Syndicate unified Mailchimp and GA4 data into PostgreSQL, powering a Tableau dashboard that delivers real-time insights and consistent metrics.
2. Improved Data Quality and Accuracy
Centralization enforces data governance. It’s easier to standardize formats, deduplicate records, and run validation checks. Fewer inconsistencies mean you’re not wasting time debating whose spreadsheet is right.
Example. Exclaimer consolidated billing and subscription info directly into Salesforce, cutting manual cleanup and improving data trust across teams.
3. Increased Efficiency and Productivity
Hunting for data kills productivity. When the information is centralized, teams spend less time asking, “Where is that file?” and more time acting on insights. Automation also reduces manual exports, imports, and data entry.
Example. NISO went from hours, sometimes days, of manual consolidation to automated overnight updates across MySQL, Excel, and QuickBooks.
4. Better Customer Experience
- A 360-degree view of the customer changes the game.
- Sales sees the full order history.
- Support sees open service tickets and shipping status.
- Marketing knows what offers actually convert.
The result? More personalized interactions, faster responses, and happier customers.
5. Enhanced Data Security and Compliance
With everything in one place, you can apply consistent access controls, encryption, and audit logging. This strategy not only strengthens security but also makes it easier to meet regulations like GDPR, HIPAA, or SOC 2.
How to Implement a Data Centralization Strategy: A Step-by-Step Guide
Centralizing data can transform your business. But it’s not just a “flip the switch” project. Here’s a roadmap to do it right.
Step 1: Define Your “Why” and Set Clear Goals and Objectives
Start with a business case, not just a tech wish list.
Ask:
- What problems are we solving?
- How will centralized data improve revenue, efficiency, or compliance?
- What will success look like in 3, 6, and 12 months?
A strong “why” keeps the project on track and gets leadership buy-in.
Step 2: Identify and Prioritize Your Data Sources
Map your data landscape: CRMs, ERPs, analytics tools, marketing platforms, spreadsheets, and APIs.
Then prioritize:
- High-impact data first (e.g., sales and financials).
- Low-complexity integrations for quick wins.
Pro tip: A visual map of your data sources makes dependencies and gaps obvious.
Step 3: Choose the Right Data Centralization Tools
The tool should fit your scale, budget, and use case.
- Data Warehouses. Optimized for structured data and analytics. Examples: Snowflake, Google BigQuery, Amazon Redshift.
- Data Lakes. Store raw, unstructured, and structured data for flexible processing.
- Data Lakehouses. The modern hybrid. They combine the structure of a warehouse with the flexibility of a lake. Tools like Databricks and Snowflake’s new features bring this to life.
Step 4: Plan and Execute Your Data Migration
Migrate in phases. Don’t try to move everything at once.
- Start with a pilot dataset.
- Validate after each step to catch issues early.
- Use automation tools to simplify the process. Platforms like Skyvia, Fivetran, or Talend Data Integration can handle replication, transformation, and scheduling with minimal manual effort.
Step 5: Establish a Robust Data Governance Framework
Centralized data without governance is just organized chaos.
- Define data ownership and access rights.
- Standardize formats and naming conventions.
- Implement monitoring and validation rules to maintain accuracy.
Step 6: Empower Your Team with Training and Support
Data centralization is only as good as the people using it.
- Train teams on how to access, query, and interpret centralized data.
- Provide clear documentation and ongoing support.
- Celebrate early wins to encourage adoption.
Common Challenges of Data Centralization and How to Overcome Them
Centralizing data is fine, but it comes with real hurdles.
Let’s consider how to tackle the common blockers head-on.
Challenge 1: High Upfront Costs and Resource Needs
The Problem. Building a central data hub often means investing in infrastructure, tools, and expertise before you’ve seen results.
The Fix. Start small with high-impact sources. Many cloud services offer pay-as-you-go models, so you can scale as you see ROI. Tools like Skyvia, Fivetran, or Stitch Data offer lightweight setup and minimal infrastructure overhead, making them practical even for lean teams.
Challenge 2: Data Migration Complexity
The Problem. Data comes from different systems, formats, or levels of cleanliness, getting it uniform and accurate is tricky and error-prone.
The Fix. Use ETL tools to validate, transform, and automate. Transformation platforms, for example, Skyvia, Talend Data Integration, or Matillion, can clean and standardize data during migration, reducing manual effort, handling deduplication, and ensuring consistency out of the box.
Challenge 3: Risk of a Single Point of Failure
The Problem. All your data living in one place can feel risky. What if that system goes down?
The Fix. Build redundancy. It could be cloud backups, multi-zone deployment, or historical snapshots. Most cloud providers (including Snowflake, BigQuery, and Redshift) offer built-in failover options to keep things resilient.
Challenge 4: Organizational Silos & Resistance to Change
The Problem. Teams often guard their data or distrust a one-size-fits-all system. Centralization can feel like “losing control.”
The Fix. Lead with benefits, not tech. Involve stakeholders early, show them what centralization saves them: time confusion. Use permission controls, so teams retain control within a unified system. Quick wins build momentum.
Best Practices for Sustainable Data Centralization
Centralizing your data is just the start; keeping it reliable and useful is where the real work happens.
1. Start Small and Iterate
Don’t try to centralize everything at once. Begin with your most critical datasets, the ones that drive decision-making or have the biggest pain points. Prove the value, then expand. This approach minimizes risk and builds momentum.
2. Prioritize Data Governance from Day One
A centralized mess is still a mess. Set standards early for data quality, naming conventions, access control, and compliance. Assign clear ownership so there’s accountability for maintaining the integrity of centralized data.
Example. Teams set up validation rules and mapping logic in Skyvia’s data flows to enforce consistent formats before data lands in the target.
3. Focus on a “Single Source of Truth”
The end goal is that everyone, from sales to finance to ops. Trusts the same numbers. Avoid multiple “versions” of reports or metrics. Consistency builds confidence and speeds up decision-making.
4. Continuously Monitor and Optimize
Data centralization isn’t a one-and-done project.
- Track performance of pipelines and queries.
- Monitor for errors or anomalies.
- Refine transformation logic as your business evolves.
- Regular check-ins keep your system efficient and relevant.
The Future of Data: The Rise of the Flexible Data Lakehouse
Data warehouses have served businesses well but they’re built for structured, predictable data. Today’s reality is messier. Companies need to handle semi-structured formats like JSON, unstructured data like documents or images, and even live streaming data. Warehouses can do it, but the cost and complexity often skyrocket.
The Best of Both Worlds
Enter the data lakehouse, a modern architecture that blends the scalability and flexibility of a data lake with the performance and governance features of a warehouse.
- From the lake side: store any type of data, raw or processed.
- From the warehouse side: query it fast, apply consistent governance, and integrate with BI tools without awkward workarounds.
Example. What Is Data Integration? explains how a unified platform helps feed clean, trusted data into any architecture, including modern lakehouses.
Flexibility and Scalability
A lakehouse grows with your needs. Start with raw data ingestion and light transformations, then scale into advanced analytics, machine learning, and real-time querying without shuffling data between systems.
Example. Some Skyvia users already use no-code pipelines to collect data from SaaS apps, databases, and APIs directly into lakehouse-ready formats. This sets them up for future adoption of Databricks, Snowflake’s lakehouse features, or similar platforms without rebuilding their pipelines.
Conclusion
Data centralization isn’t just a technical project but a business advantage.
Done right, it:
- Gives you one source of truth for decision-making.
- Improves data quality with consistent governance.
- Saves time and boosts productivity across teams.
- Enhances customer experiences with complete, accurate insights.
- Strengthens security and compliance by managing access in one place.
The path to success is clear:
- Start small, targeting high-impact data sources.
- Put governance first so your central hub stays clean.
- Build for scalability and resilience — not just today’s needs.
- Monitor and refine so it keeps delivering value as your business evolves.
In a world where speed and accuracy win, you can’t afford scattered, unreliable data. The sooner you break down silos, the faster you can move from chasing numbers to acting on them.
Ready to unify data?
Explore Skyvia and start building your single source of truth.
F.A.Q. for Data Centralization
What is the difference between a data warehouse and a data lake?
A data warehouse stores structured, processed data for fast querying. A data lake stores raw, unstructured, or semi-structured data for flexible use. A lakehouse combines both.
What is the most important first step in a data centralization project?
Define your business goals and identify high-impact data sources to start with. Clear priorities ensure a focused, effective rollout.
Is data centralization only for large enterprises?
No. Cloud-based, pay-as-you-go tools make centralization affordable for small and mid-sized businesses, not just big corporations.
What are the main disadvantages of a centralized data system?
Potential single point of failure, upfront costs, and cultural resistance. These can be mitigated with backups, phased rollout, and stakeholder engagement.
Can you give a simple example of data centralization in action?
Syncing customer, sales, and billing data from multiple apps into one dashboard so sales, support, and finance teams work from the same, accurate information.


